Blown Out Vein From Blood Draw
Blown Out Vein From Blood Draw - Web if you're having your procedure done in a hospital or healthcare setting, there's a good chance that your blood will be drawn by a phlebotomist, one who specializes in drawing blood, according to diane crawford, ceo and founder of. Specifically, the median cubital vein, located between the cephalic and basilic vein, is a large vein suitable for blood sampling. Once that happens, the needle. Peripheral veins, typically the antecubital veins, are the usual sites for venous blood sampling. Web a blown vein is a vein that has been ruptured and is leaking blood. In superficial thrombophlebitis, the vein is near the surface of the skin. Web until it has time to heal, that vein can’t be used to for blood draws , intravenous (iv) line insertion, or injection of medication. Symptoms include bruising, swelling and discomfort around your vein. Web blown veins occur when a needle injures or irritates a vein, causing blood to leak into the surrounding area. Is sudden loss of blood pressure a symptom of a blown vein? Web if you're having your procedure done in a hospital or healthcare setting, there's a good chance that your blood will be drawn by a phlebotomist, one who specializes in drawing blood, according to diane crawford, ceo and founder of. Web until it has time to heal, that vein can’t be used to for blood draws , intravenous (iv) line. Web until it has time to heal, that vein can’t be used to for blood draws , intravenous (iv) line insertion, or injection of medication. When the vein starts to leak, you’ll notice your skin darkening around the insertion site. This swelling is often accompanied by discoloration or bruising to the area. Once that happens, the needle. In the majority. Here, we’ll look into the causes and symptoms of a blown vein, as well as how it can be prevented. A bruise may appear after a blood draw if small blood vessels get damaged when the needle gets inserted or if there isn’t enough pressure applied after the needle is removed. Web the most obvious symptom of a blown vein. Ultrasound guidance, when equipment and trained personnel are available, can facilitate blood sampling from deep, nonpalpable veins. In the majority of cases, a blown vein is not dangerous, but it should be treated. In most cases, a blown vein is caused by a healthcare professional inserting a needle into the vein. Web venous bleeding can be caused by the following. Once that happens, the needle. First aid for a bleeding vein. Web in these instances, blood leaks out of the vein, causing swelling, bruising and tenderness. Thrombophlebitis is due to one or more blood clots in a vein that cause inflammation. Web if you're having your procedure done in a hospital or healthcare setting, there's a good chance that your. Dvt increases the risk of serious health problems. Web blown veins occur when a needle injures or irritates a vein, causing blood to leak into the surrounding area. Web superficial thrombophlebitis is an inflammation of a vein just below the surface of the skin, which results from a blood clot. Web a blown vein is a vein that’s mildly injured. In the majority of cases, a blown vein is not dangerous, but it should be treated. This is what’s called a “blown vein,” and once a vein is “blown,” it cannot be used to deliver medication or to draw blood until it’s completely healed. Web a vein in the antecubital fossa is one of the first choices for routine blood. Symptoms include bruising, swelling and discomfort around your vein. While this may sound severe, it is uncommon and not usually severe. As a result, it causes the vein to be useless to draw blood, inject medication, or use an iv. Ultrasound guidance, when equipment and trained personnel are available, can facilitate blood sampling from deep, nonpalpable veins. Specifically, the median. Web thrombophlebitis is a condition that causes a blood clot to form and block one or more veins, often in the legs. This condition may occur after recently using an iv line, or after trauma to the vein. Thrombophlebitis is due to one or more blood clots in a vein that cause inflammation. Peripheral veins, typically the antecubital veins, are. Web venous bleeding can be caused by the following wounds: This condition may occur after recently using an iv line, or after trauma to the vein. However, when a vein blows, the needle must be removed immediately. Symptoms include bruising, swelling and discomfort around your vein. Since the fluids are seeping out of the vein, they have a tendency to. Web a blown vein is a vein that’s mildly injured during a blood draw or iv placement. A collapsed vein can usually be recovered by using techniques such as arm dangling or a warm compressed. Ultrasound guidance, when equipment and trained personnel are available, can facilitate blood sampling from deep, nonpalpable veins. Web thrombophlebitis is a condition that causes a blood clot to form and block one or more veins, often in the legs. Once that happens, the needle. Peripheral veins, typically the antecubital veins, are the usual sites for venous blood sampling. Web a blown vein occurs when the wall of the vein has been punctured and blood escapes from the vein to create a hematoma. A bruise may appear after a blood draw if small blood vessels get damaged when the needle gets inserted or if there isn’t enough pressure applied after the needle is removed. Web a blown vein refers to a vein that has been damaged or ruptured during a medical procedure, such as phlebotomy blood draw procedures or administering an intravenous (iv) line. While this may sound severe, it is uncommon and not usually severe. The bruising will gradually get lighter and disappear within 10 to 12 days. In the majority of cases, a blown vein is not dangerous, but it should be treated. Web a blown or ruptured vein occurs when a vein gets punctured and it causes blood to leak outside the vein. In most cases, you are likely to experience only minor discomfort that lasts a couple of days. Symptoms of a blown vein include discolored skin around the injection site, bruising, swelling, localized pain, and a stinging sensation. Web a vein in the antecubital fossa is one of the first choices for routine blood sampling in adults.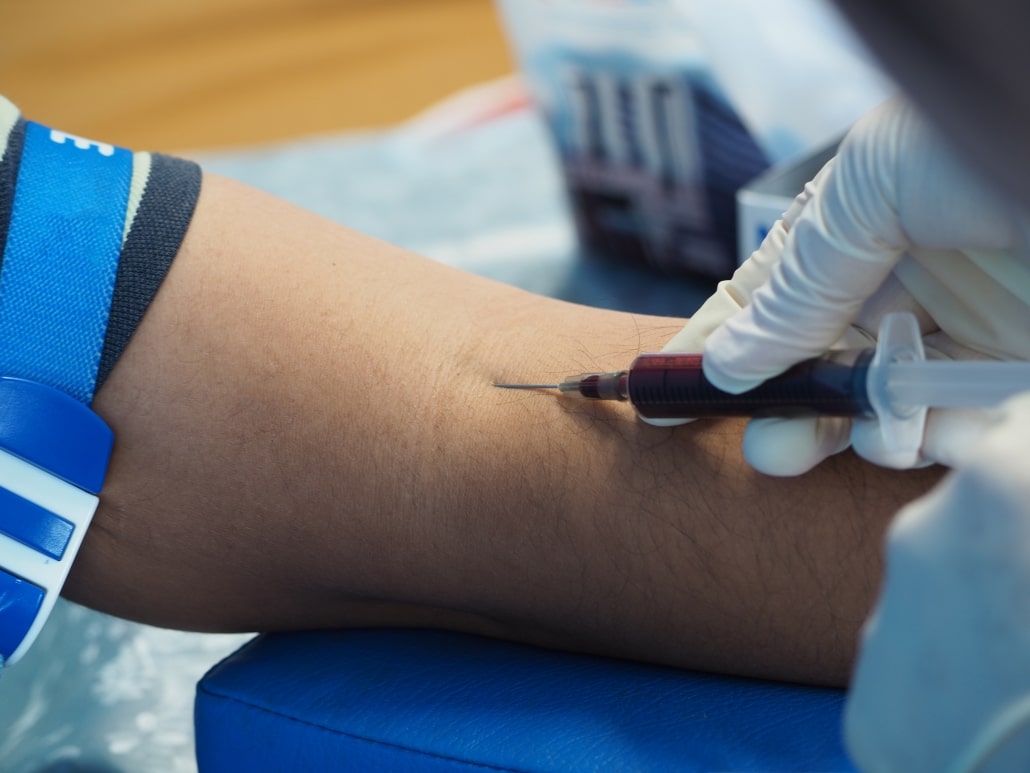
How to draw blood from a patient’s vein as painlessly as possible

Blown Veins Explained E Phlebotomy Training

how to draw blood from a vein? YouTube

How to Draw Blood from Hard to Hit Veins 15 Steps (with Pictures)
Blown Veins Explained E Phlebotomy Training
How to draw blood from a patient’s vein as painlessly as possible
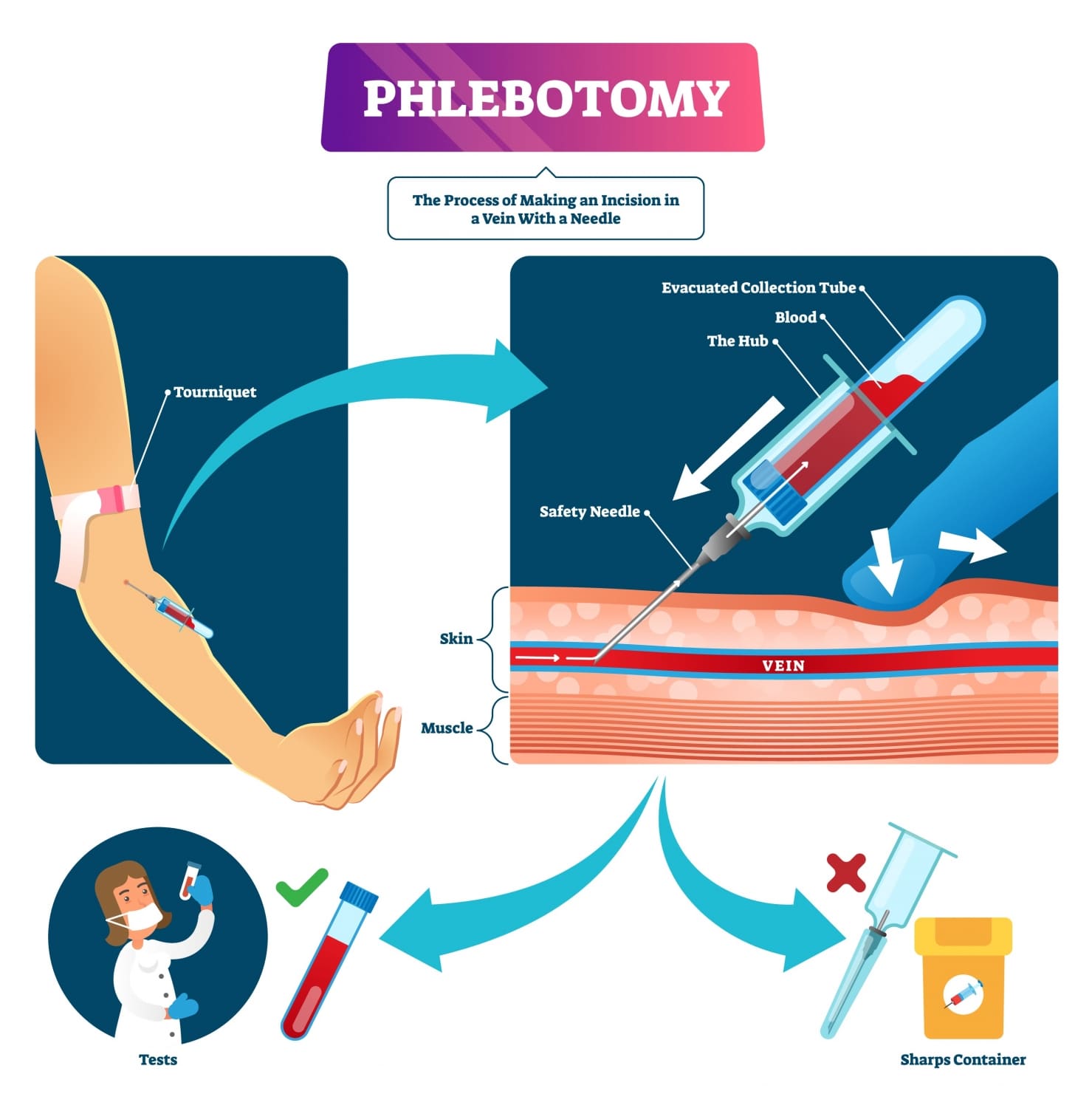
Are blown veins harmful? Symptoms, causes, and treatment

What is a Collapsed Vein Vs Blown Vein NursingTroop
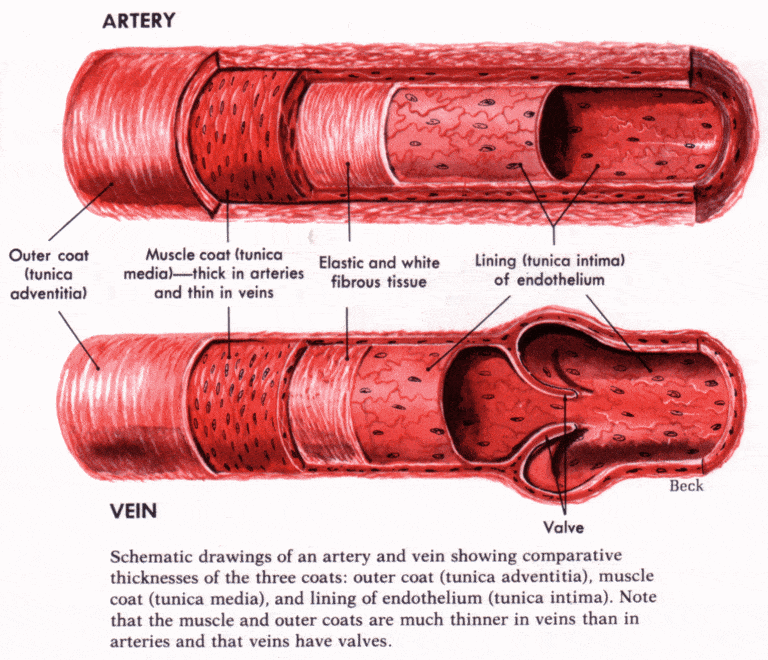
Why Do Veins Blow When Drawing Blood Joseph Ouldives

Blown Veins Explained E Phlebotomy Training
Web A Blown Vein, Or A Ruptured Vein, Is A Vein That A Needle Has Damaged.
In Most Cases, A Blown Vein Is Not.
Specifically, The Median Cubital Vein, Located Between The Cephalic And Basilic Vein, Is A Large Vein Suitable For Blood Sampling.
As A Result, It Causes The Vein To Be Useless To Draw Blood, Inject Medication, Or Use An Iv.
Related Post:
