Draw The Major Organic Product Of The Following Friedelcrafts Alkylation
Draw The Major Organic Product Of The Following Friedelcrafts Alkylation - Carbohydrates · institutional · chemistry · psychology Web the rearrangements occur due to hydride shifts and methyl shifts. Draw the structure(s) of the major neutral organic product(s) obtained after workup of the following… a: (an excess of benzene is present.) do not draw any. Web the electrophilic substitution reaction between benzene and chloromethane. Secondary and teriary halides only form the free. Identify the aromatic compound, and the reagent and catalyst. The first step creates a cabocation that acts as the electrophile in the reaction. We start with our alkyl chloride and we add our aluminum chloride, which we've already seen can function as a lewis. (an excess of benzene is present.) do not draw any aluminum byproducts. (an excess of benzene is present.) do not draw any. Web the electrophilic substitution reaction between benzene and chloromethane. ) do not draw any aluminum byproducts. (an excess of benzene is present.) **hint given:this reaction is an electrophilic aromatic. Carbohydrates · institutional · chemistry · psychology We start with our alkyl chloride and we add our aluminum chloride, which we've already seen can function as a lewis. (an excess of benzene is present.) **hint given:this reaction is an electrophilic aromatic. Secondary and teriary halides only form the free. (an excess of benzene is present.) do not draw any. Carbohydrates · institutional · chemistry · psychology This step activates the haloalkane. The first step creates a cabocation that acts as the electrophile in the reaction. Web the rearrangements occur due to hydride shifts and methyl shifts. We start with our alkyl chloride and we add our aluminum chloride, which we've already seen can function as a lewis. ) do not draw any aluminum byproducts. (an excess of benzene present: (an excess of benzene is present.) **hint given:this reaction is an electrophilic aromatic. This step activates the haloalkane. Secondary and teriary halides only form the free. Web the rearrangements occur due to hydride shifts and methyl shifts. (an excess of benzene present: (an excess of benzene is present.) **hint given:this reaction is an electrophilic aromatic. (an excess of benzene is present.) do not draw any. This step activates the haloalkane. Web the electrophilic substitution reaction between benzene and chloromethane. ) do not draw any aluminum byproducts. (an excess of benzene is present.) do not draw any. The first step creates a cabocation that acts as the electrophile in the reaction. Draw the major and minor product. (an excess of benzene is present.) do not draw any. Draw the major and minor product. Web the electrophilic substitution reaction between benzene and chloromethane. (an excess of benzene is present.) do not draw any. (an excess of benzene is present.) do not draw any aluminum byproducts. Web the rearrangements occur due to hydride shifts and methyl shifts. (an excess of benzene is present.) do not draw any. (an excess of benzene is present.) do not draw any aluminum byproducts. Secondary and teriary halides only form the free. We start with our alkyl chloride and we add our aluminum chloride, which we've already seen can function as a lewis. (an excess of benzene is present;) do not draw. (an excess of benzene is present.) **hint given:this reaction is an electrophilic aromatic. Identify the aromatic compound, and the reagent and catalyst. (an excess of benzene is present.) do not draw any. Draw the major and minor product. The first step creates a cabocation that acts as the electrophile in the reaction. Identify the aromatic compound, and the reagent and catalyst. Web the electrophilic substitution reaction between benzene and chloromethane. Web the rearrangements occur due to hydride shifts and methyl shifts. Draw the structure(s) of the major neutral organic product(s) obtained after workup of the following… a: ) do not draw any aluminum byproducts. (an excess of benzene is present;) do not draw any aluminum byproducts. ) do not draw any aluminum byproducts. Web the rearrangements occur due to hydride shifts and methyl shifts. Web the electrophilic substitution reaction between benzene and chloromethane. Draw the structure(s) of the major neutral organic product(s) obtained after workup of the following… a: This step activates the haloalkane. (an excess of benzene is present.) do not draw any aluminum byproducts. We start with our alkyl chloride and we add our aluminum chloride, which we've already seen can function as a lewis. Carbohydrates · institutional · chemistry · psychology (an excess of benzene is present.) do not draw any. Identify the aromatic compound, and the reagent and catalyst. (an excess of benzene is present.) do not draw any. (an excess of benzene present: Draw the major and minor product.[Solved] Predict the major product of the following Friede

FriedelCrafts Alkylation Reaction Mechanism With Examples
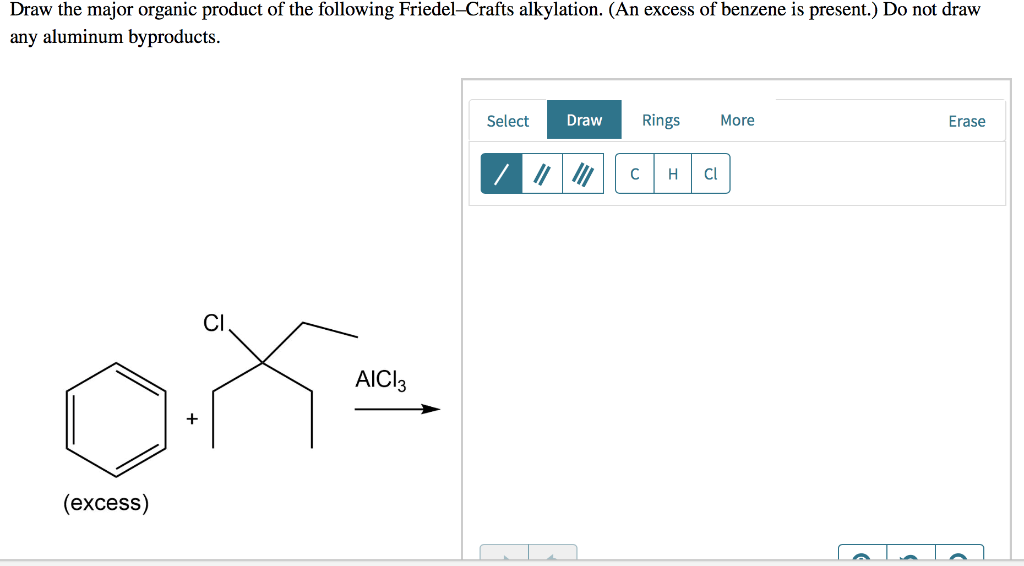
Solved Draw the major organic product of the following
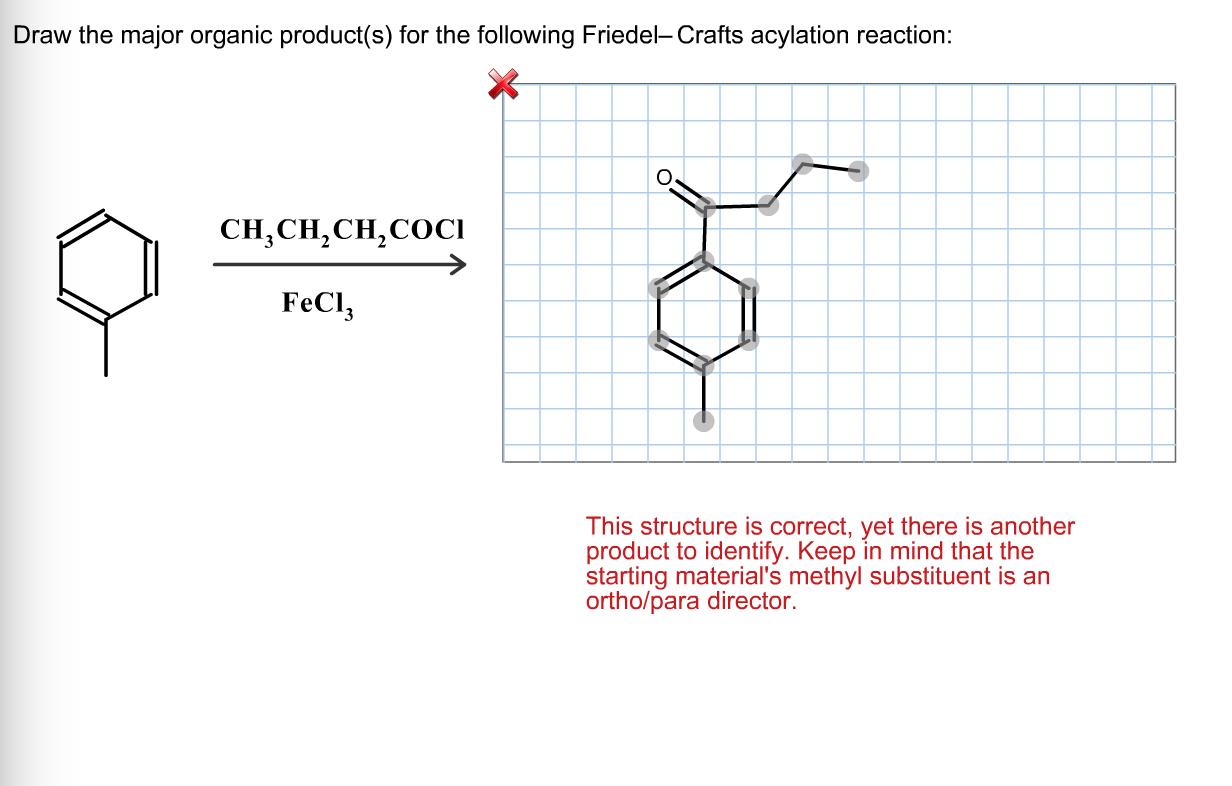
Solved draw the major organic products for the following
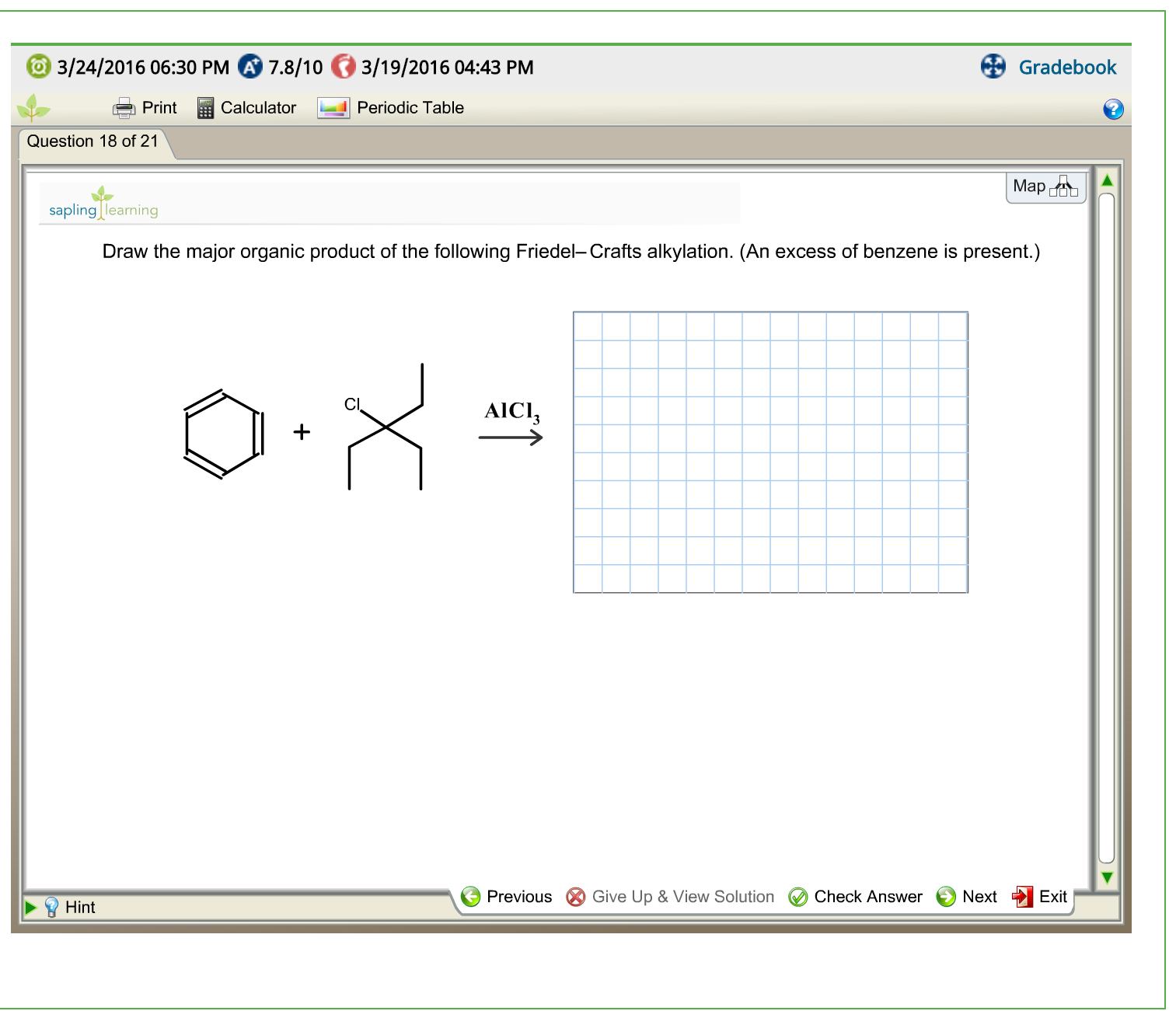
Solved Draw the major organic product of the following
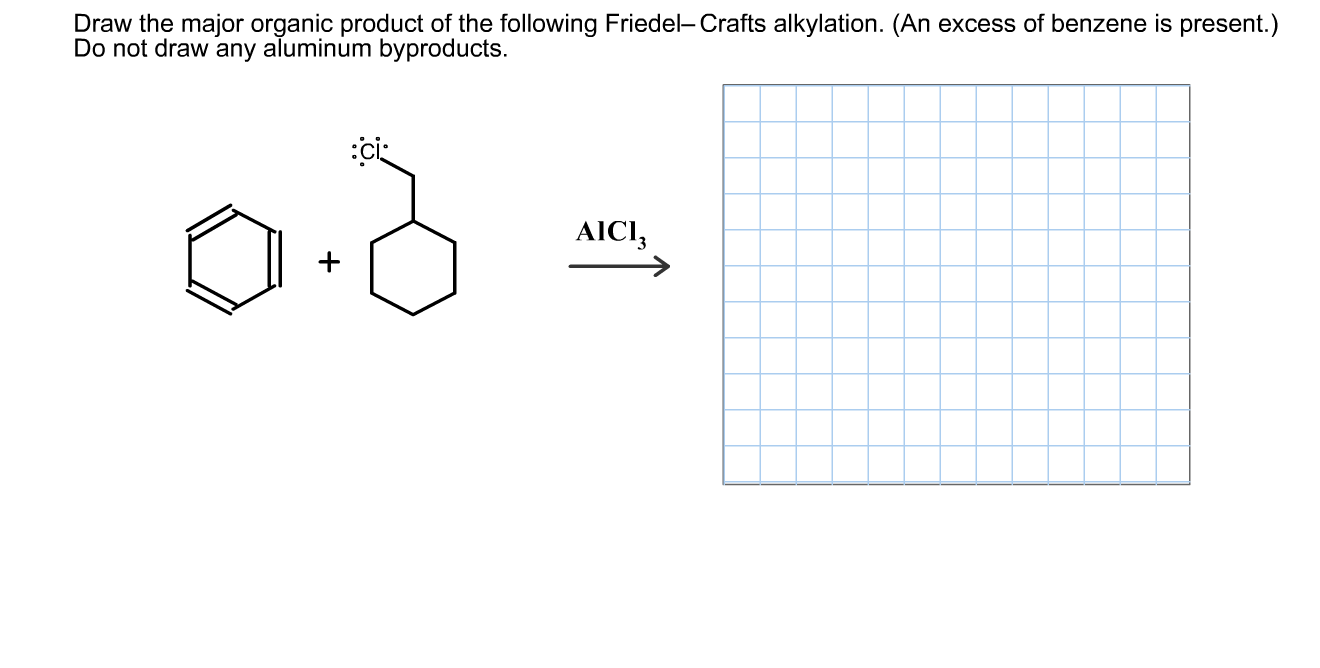
Solved Draw the major organic product of the following
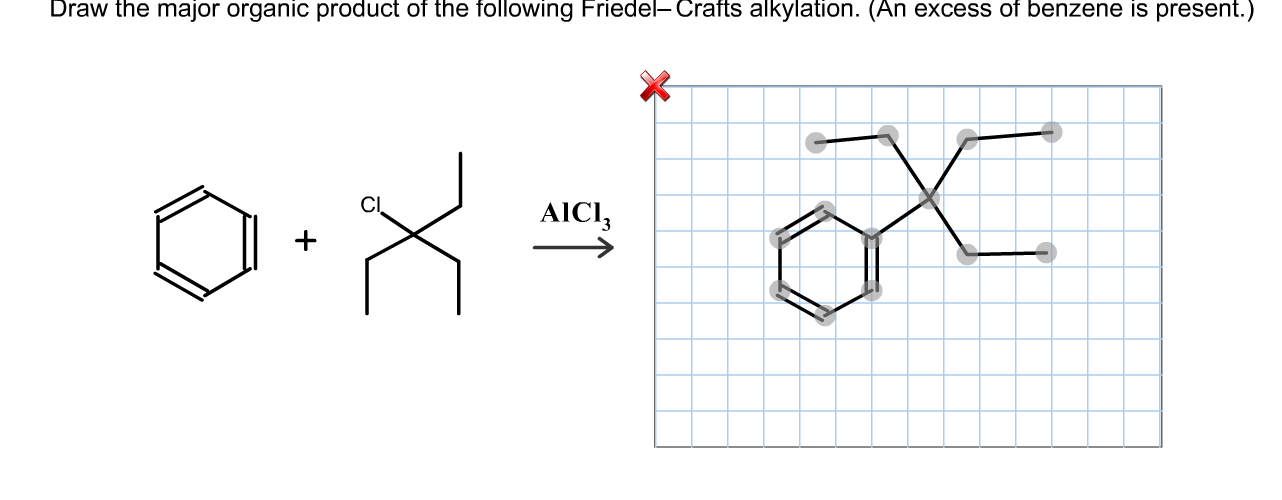
Solved Draw the major organic product of the following
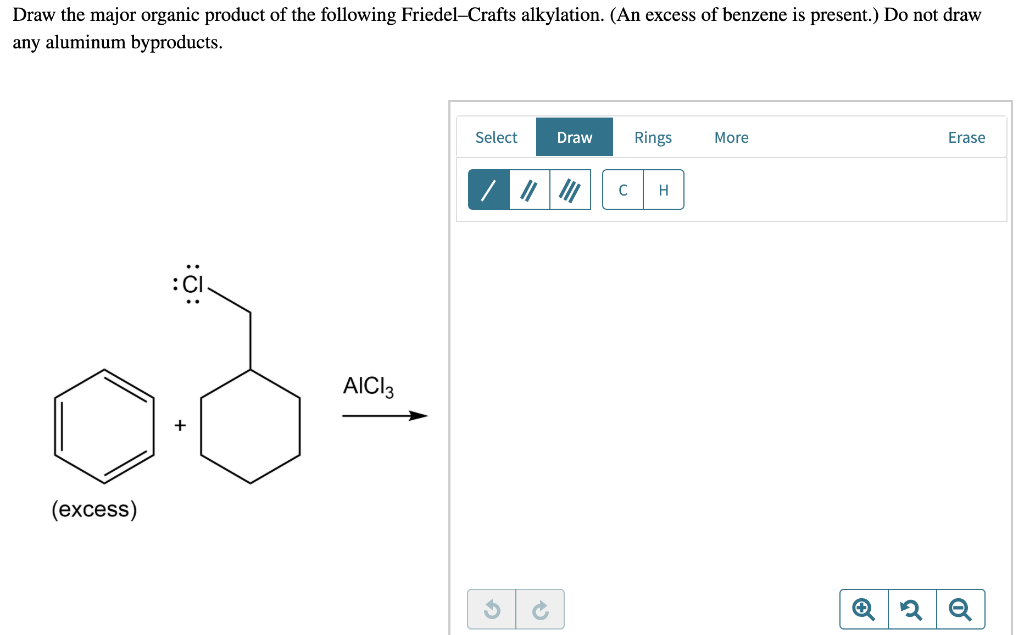
Solved Draw the major organic product of the following
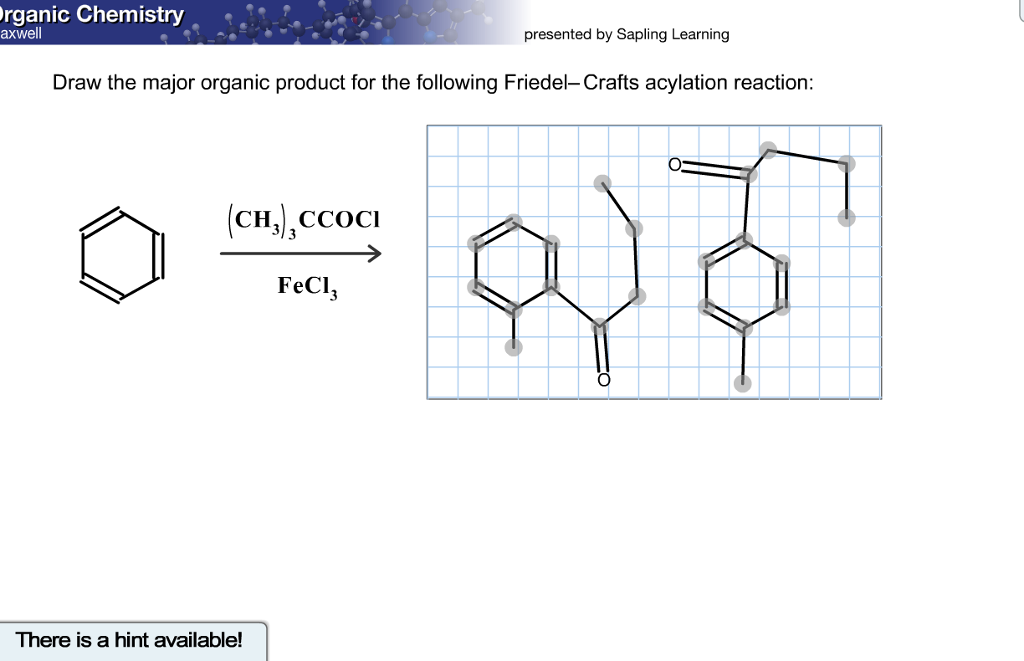
Solved Draw The Major Organic Product For The Following F...
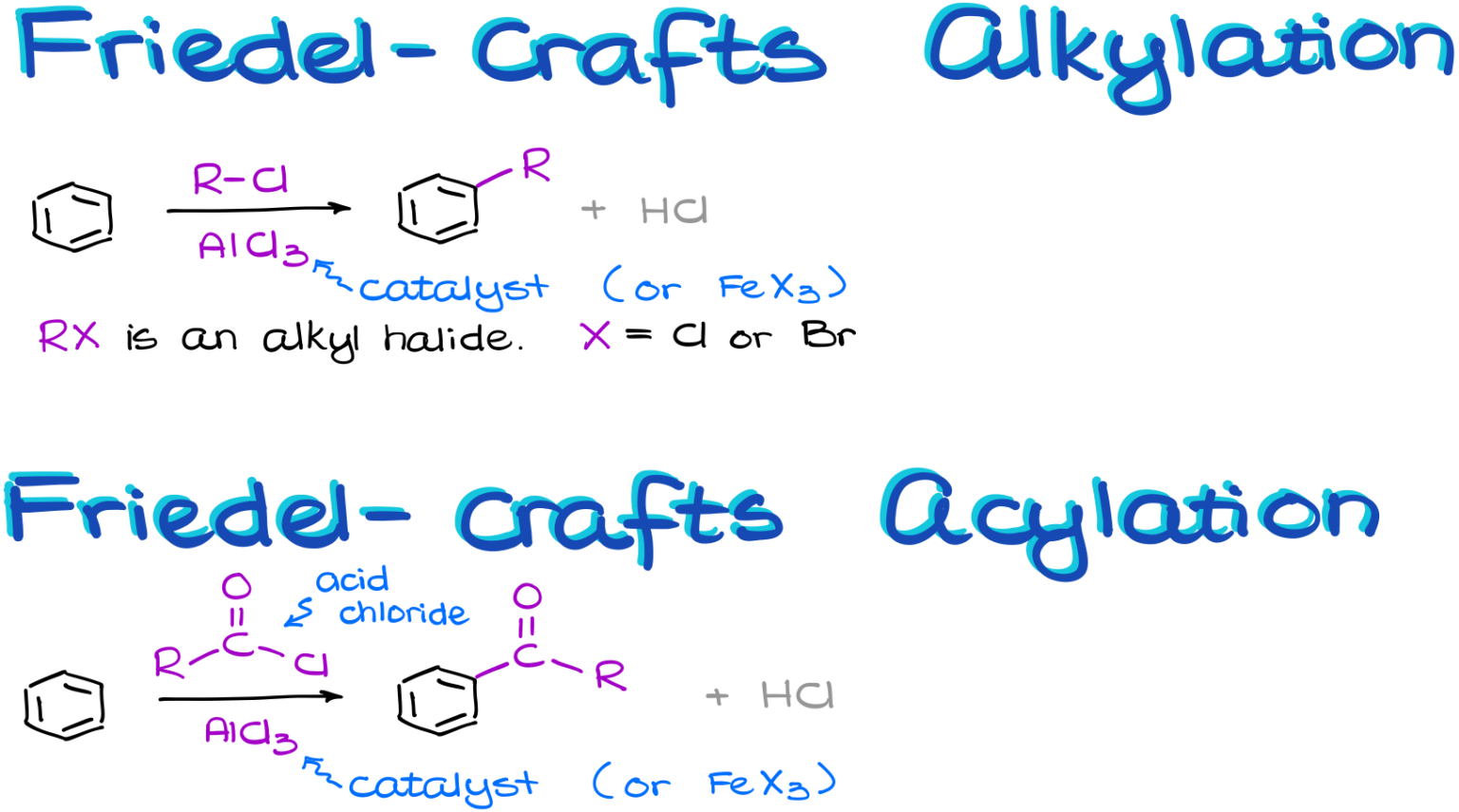
FriedelCrafts Alkylation and Acylation Reaction — Organic Chemistry Tutor
The First Step Creates A Cabocation That Acts As The Electrophile In The Reaction.
(An Excess Of Benzene Is Present.) Do Not Draw Any.
(An Excess Of Benzene Is Present.) **Hint Given:this Reaction Is An Electrophilic Aromatic.
Secondary And Teriary Halides Only Form The Free.
Related Post:
![[Solved] Predict the major product of the following Friede](https://media.cheggcdn.com/study/972/97296626-082c-4771-b84e-66108f8f4f98/image)