Drawing Free Body Diagrams Answer Key
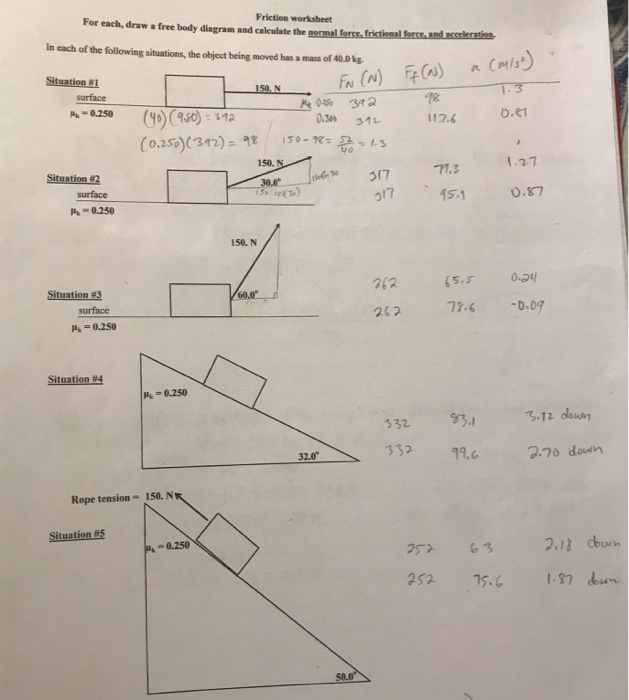
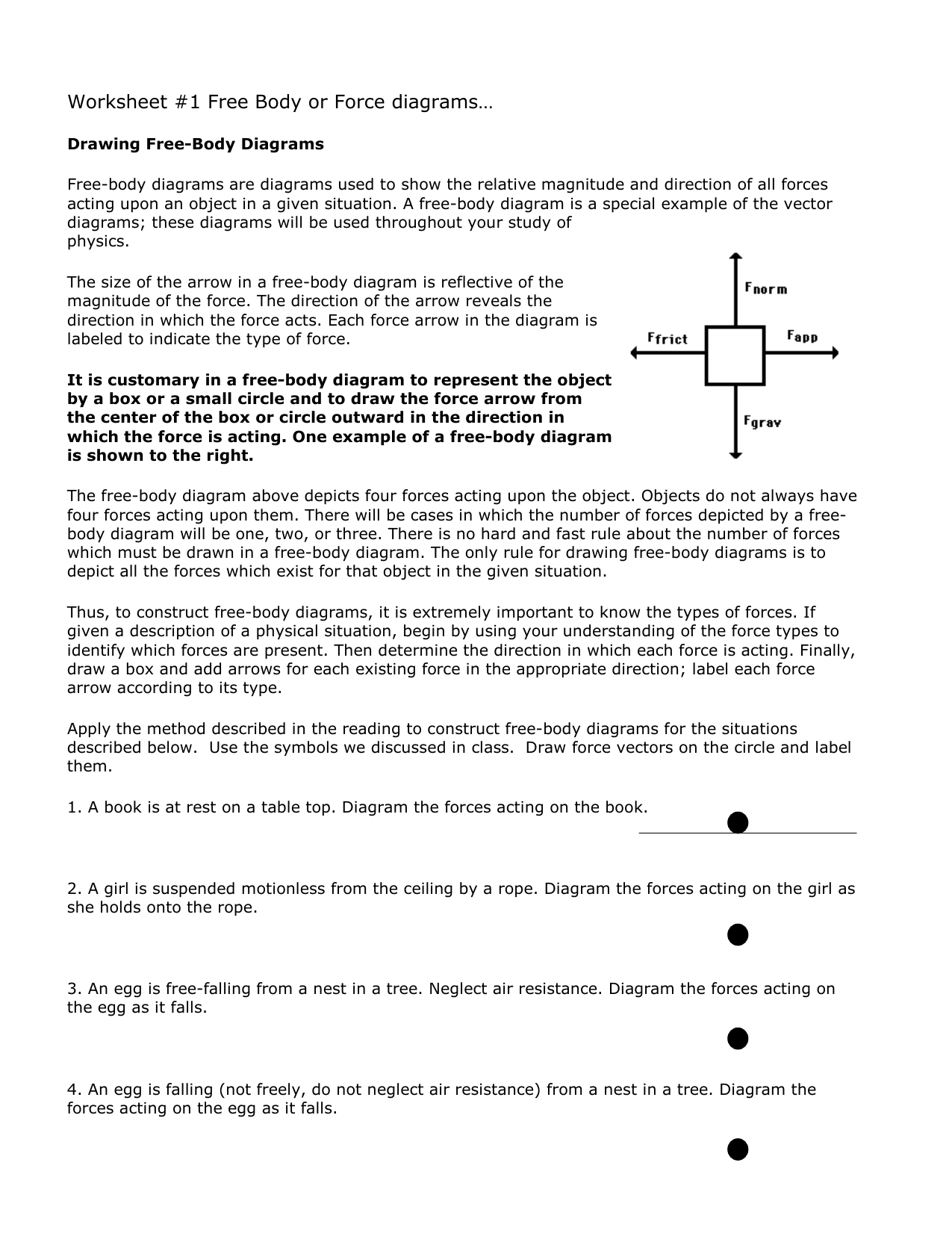
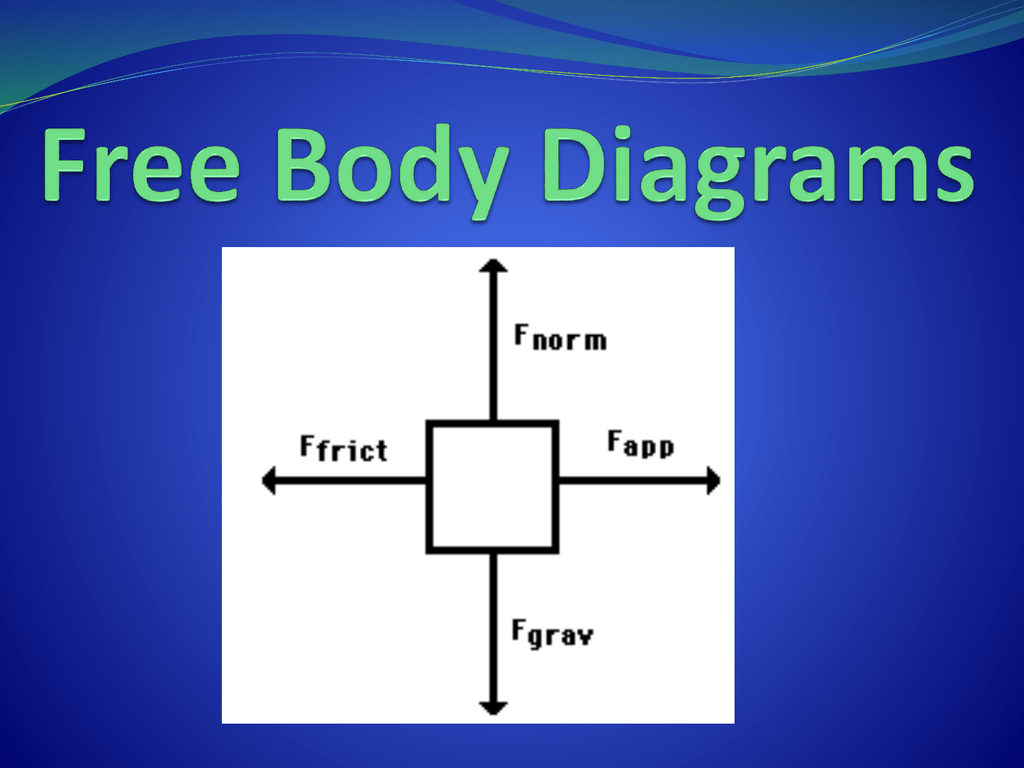
Drawing Free Body Diagrams Answer Key - Include at least 4 forces and their magnitudes. Coulomb's law describes the force of attraction (or repulsion) experienced between two charged point objects. These diagrams will be used throughout your study of physics. This product comes in 2 formats: A 1.0 kg book is at rest on a tabletop. Given a scenario or a graph, sketch all four graphs. Web whether you are a student studying physics or an engineer working on complex structures, being able to accurately draw and interpret free body diagrams is crucial. That is, f net = 0 f net = 0) or newton’s second law if the body is accelerating (unbalanced force; Use the notation in the image as subscripts when labeling forces. Explain how the graphs relate to one another. Deciding upon the relative size of opposing forces, 4. Web free body diagrams can be drawn in two ways: Explain how the graphs relate to one another. Include at least 4 forces and their magnitudes. 1) by representing the object as a point mass and drawing arrows pointing outward from the dot to represent the forces acting on an object. Web whether you are a student studying physics or an engineer working on complex structures, being able to accurately draw and interpret free body diagrams is crucial. Determine the magnitude of all forces and fill in the blanks. Web in this activity you will practice creating free body diagrams (fbd) in order to evaluate all of the forces interacting with. Explain how the graphs relate to one another. Diagram the forces acting on the book. Web free body diagrams can be drawn in two ways: Include at least 4 forces and their magnitudes. Draw a free body diagram for both objects. Determine the magnitude of all forces and fill in the blanks. We visit a bustling port on georgia's coast to illustrate how free body diagrams help us analyze forces. Explain how the graphs relate to one another. 6 min read • january 5, 2023. Coulomb's law describes the force of attraction (or repulsion) experienced between two charged point objects. Include at least 4 forces and their magnitudes. Given a scenario or a graph, sketch all four graphs. Coulomb's law describes the force of attraction (or repulsion) experienced between two charged point objects. Given a scenario or a graph, sketch all four graphs. Additional resources and ideas for incorporating free body diagrams into an instructional unit on newton's second law. From physics in motion, unit 3. This product comes in 2 formats: Web in this activity you will practice creating free body diagrams (fbd) in order to evaluate all of the forces interacting with those objects. 1.1 the scope and scale from physics; View this simulation to predict, qualitatively, how an external force will affect the speed and direction of. Additional resources and ideas for incorporating free body diagrams into an instructional unit on newton's second law can be found at the teacher toolkits section of the physics classroom website. Web 10 sample situations that students read and draw free body diagrams for objects that are stationary or moving. Deciding upon the relative size of opposing forces, 4. These diagrams. In this guide, we will use the first way of drawing. Draw a free body diagram for both objects. 1.1 the scope and scale from physics; Given a scenario or a graph, sketch all four graphs. Explain how the graphs relate to one another. We visit a bustling port on georgia's coast to illustrate how free body diagrams help us analyze forces. Web the motion of objects is determined by the relative size and the direction of the forces that act upon it. Drawing a force diagram with arrows having a labeled force type and the proper size From physics in motion, unit 3.. Web the motion of objects is determined by the relative size and the direction of the forces that act upon it. Coulomb's law describes the force of attraction (or repulsion) experienced between two charged point objects. Given a scenario or a graph, sketch all four graphs. Identifying the types of forces acting on the object, 2. View this simulation to. View this simulation to predict, qualitatively, how an external force will affect the speed and direction of an object’s motion. Web 10 sample situations that students read and draw free body diagrams for objects that are stationary or moving. Numerous examples, illustrations, and animations assist in the explanations. A 1.0 kg book is at rest on a tabletop. 1) by representing the object as a point mass and drawing arrows pointing outward from the dot to represent the forces acting on an object and 2) by drawing the forces on an object specifically at the point where they are exerted on the object. The basics, plus all the classic misconceptions! Explain how the graphs relate to one another. In this guide, we will use the first way of drawing. That is, f net ≠ 0 f net ≠ 0 ). From physics in motion, unit 3. Given a scenario or a graph, sketch all four graphs. Useful rules for drawing free body diagrams are also explained. Background information and activity sheet for students 1.3d. These diagrams will be used throughout your study of physics. Drawing a force diagram with arrows having a labeled force type and the proper size Web whether you are a student studying physics or an engineer working on complex structures, being able to accurately draw and interpret free body diagrams is crucial.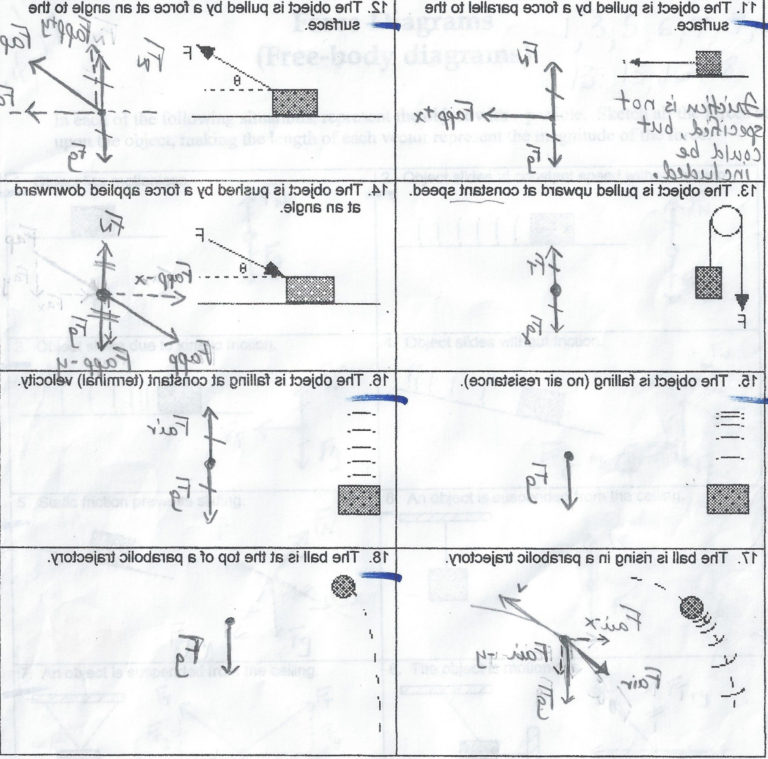
Physics Free Body Diagram Worksheet Geekchicpro —

Labster Forces And Free Body Diagram Answer Key
14+ free body diagram worksheet answers GavinZichen

Free Body Diagram Worksheet Answers

How to Solve Drawing FreeBody Diagrams Worksheet Answers Revealed!
Free Body Diagram Worksheet Answers
drawing freebody diagrams worksheet answers educaxcontic
Free Body Diagram Worksheet Answers

Drawing Free Body Diagrams Physics Classroom Answers Introduction To

The Physics Classroom Free Body Diagrams Answer Key
Explain How The Graphs Relate To One Another.
Diagram The Forces Acting On The Book.
Label Each Arrow To Indicate The Type Of Force.
This Product Comes In 2 Formats:
Related Post:
