Drawing Lens
Drawing Lens - So you see your paper and the subject at the same time. The video lesson answers the following questions: Draw the object relative to the lens and label the focal length on either. This video explores the concept of convex lenses, focusing on how they refract and transmit light. Though garcia has used and researched camera lucidas for more than a decade, the duo was. Web this demonstration lets you visualize the ray diagrams for converging and diverging lenses. Draw the third ray to the exact center of the lens. The instructor explains the behavior of light as it passes through a lens, using the analogy of a car to illustrate refraction. You will need to adjust the lengths and angles of your 5 lines depending on perspective. This video breaks down how convex lenses form images. The lucy drawing tool is an improved adaptation of the classic camera lucida. Place arrowheads upon the rays to indicate their direction of travel. Web the focal length of the lens is the distance from the center of the lens to the spot, given to be 8.00 cm. See camera lens drawing stock video clips. The instructor demonstrates how rays. You will need to adjust the lengths and angles of your 5 lines depending on perspective. Once these incident rays strike the lens, refract them according to the three rules of refraction for double concave lenses. Draw two small rectangles & an oval. Landscape, portrait, still life, and more. See camera lens drawing stock video clips. These parameters are specified in production drawings to ensure the lens meets performance requirements. We define the ratio of image height to object height ( hi / ho) as the magnification m. Often due to poor drawing skills students lose marks in ray diagrams. Camera, lens, objects, everyday, camera with lens, how to draw everyday objects. Then, we substitute this. Use the 5 lines to work out your basic shape. Web the drawing ray diagrams for converging lenses video tutorial reviews the three rules of refraction for converging lenses and demonstrates how to use the rules to draw a ray diagram for varying locations along the principal axis of a converging lens. The symbol ↕ used to draw the ray. Start with the sphere and imagine the eyelids wrapping around the sphere. How does a lens or mirror form an image? Web to obtain numerical information, we use a pair of equations that can be derived from a geometric analysis of ray tracing for thin lenses. You will need to adjust the lengths and angles of your 5 lines depending. Complete the ray diagram by drawing where the image of this object will be seen. Web an object is placed outside the focal point of a concave lens. Basically, the lucy enables you to see two things at the same time laid over each other. Web this demonstration lets you visualize the ray diagrams for converging and diverging lenses. Web. Draw the object relative to the lens and label the focal length on either. How does a lens or mirror form an image? The instructor explains the behavior of light as it passes through a lens, using the analogy of a car to illustrate refraction. By manipulating the object and lens locations, you can create real or virtual images. Camera,. So you see your paper and the subject at the same time. How does a lens or mirror form an image? (25.6.2) (25.6.2) f = 8.00 c m. By manipulating the object and lens locations, you can create real or virtual images. Place arrowheads upon the rays to indicate their direction of travel. 1 do + 1 di = 1 f (24.3.1) (24.3.1) 1 d o + 1 d i = 1 f. Pick a point on the top of the object and draw three incident rays traveling towards the. Once these incident rays strike the lens, refract them according to the three rules of refraction for double concave lenses. Web an object. Web this study aims to explore the meanings communicated by young children with visual cultural semiotic resources available in the science classroom. Observe how the image changes when you adjust the focal length of the lens, move the object, or move the screen. Web in this tutorial, you will learn how to draw camera with lens. Once these incident rays. By manipulating the object and lens locations, you can create real or virtual images. The video lesson answers the following questions: 1 do + 1 di = 1 f (24.3.1) (24.3.1) 1 d o + 1 d i = 1 f. Draw a rectangle and a horizontal shape as shown. Once these incident rays strike the lens, refract them according to the three rules of refraction for double concave lenses. This video explores the concept of convex lenses, focusing on how they refract and transmit light. Works for draw, painting, or any other medium. We focus on the analysis of two. Simulation of image formation in concave and convex lenses. Start with the sphere and imagine the eyelids wrapping around the sphere. Observe how the image changes when you adjust the focal length of the lens, move the object, or move the screen. Serving as an art tracing tool. The instructor demonstrates how rays refract through the lens, forming real, inverted, or virtual images. Move the point named focus' to the right side of the lens to change to a concave lens. The video also introduces the idea of a lens's focal point and the thin lens assumption. Web the focal length of the lens is the distance from the center of the lens to the spot, given to be 8.00 cm.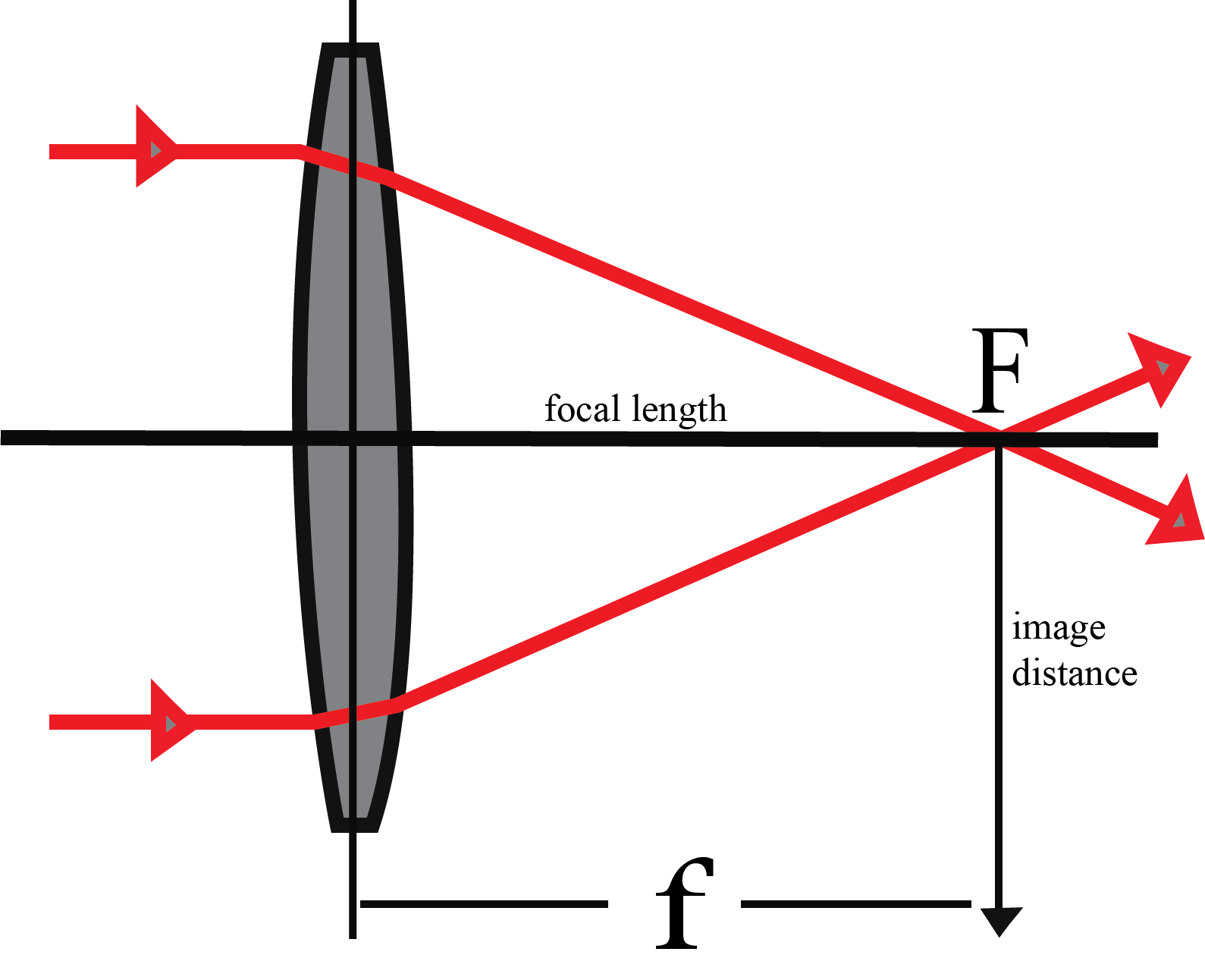
How To Draw A Ray Diagram For A Convex Lens

Camera Lens Drawing at Explore collection of
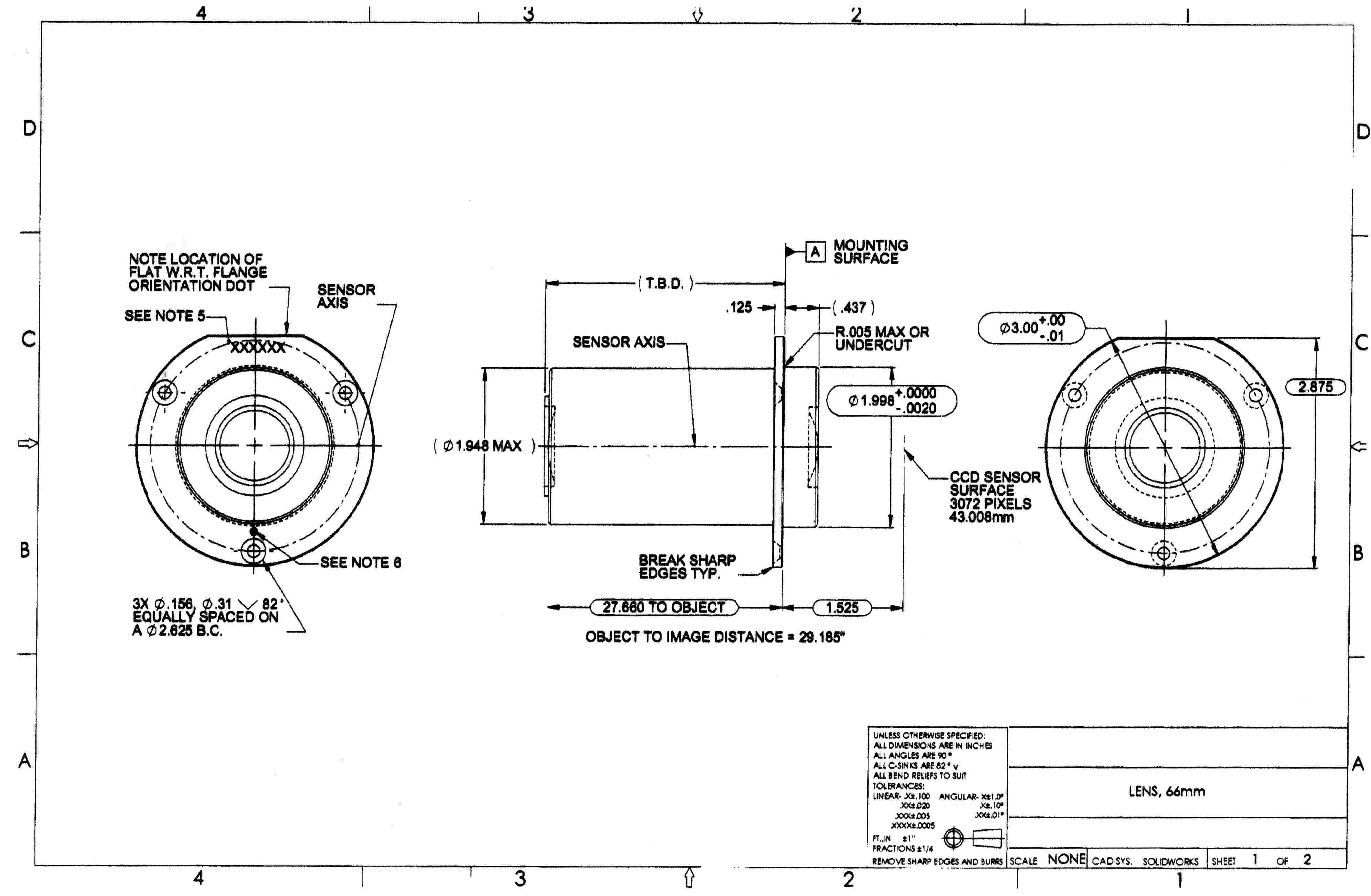
How to read an optics production drawing — Optics for Hire
Lens Drawing at Explore collection of Lens Drawing

Drawing Lens Ray Diagrams King David High School YouTube

How To Draw Camera Lens at How To Draw
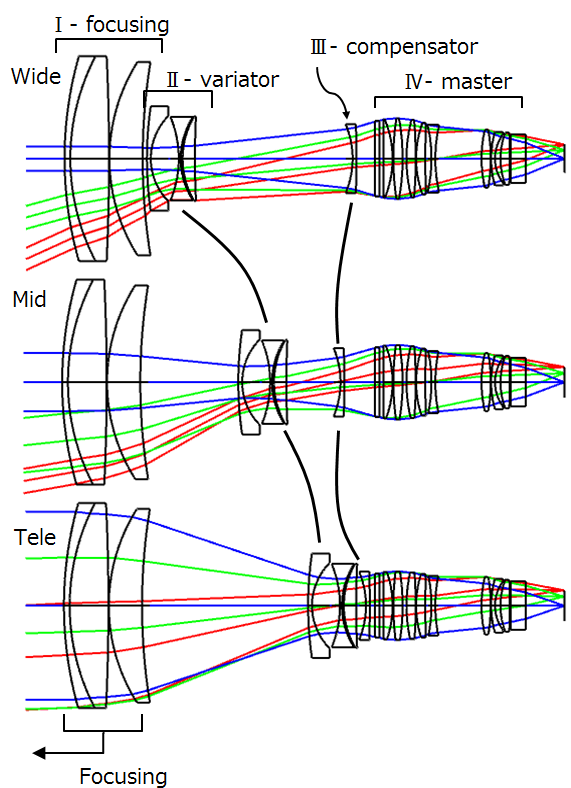
Optical Lens Design Forms An Ultimate Guide to the types of lens design
Lens Drawing at GetDrawings Free download

Rules for drawing Ray Diagram in Convex and Concave Lens Teachoo

Description Convex and concave lens, vector illustration diagrams
Draw The Third Ray To The Exact Center Of The Lens.
Complete The Ray Diagram By Drawing Where The Image Of This Object Will Be Seen.
Identify The Focal Length Of The Concave Lens ( F) And The Distance From The Center Of The Lens ( D ).
It Explores Different Scenarios Where An Object Is Placed At Various Distances From The Lens.
Related Post:
