Elastic Connective Tissue Drawing
Elastic Connective Tissue Drawing - Web histology of dense regular connective tissue The organic matrix is similar to the matrix material found in other connective tissues, including some amount of collagen and elastic fibers. Slide 36 (aorta, aldehyde fuchsin) view virtual slide. This is a loose connective tissue that consists of fat cells with little extracellular matrix. A vital liquid flowing in the bodies of many types of animals. Web supportive connective tissue —bone and cartilage—provide structure and strength to the body and protect soft tissues. • understand how the structure of connective tissue is related to its function. Web connective tissue is the tissue that connects or separates, and supports all the other types of tissues in the body. Be aware that there are many ways to categorize connective tissues, and, in some cases, intertextual nomenclature variation exists. Web brown adipose tissue is thermogenic, meaning that as it breaks down fats, it releases metabolic heat, rather than producing adenosine triphosphate (atp), a key molecule used in metabolism. Web connective tissue is the tissue that connects or separates, and supports all the other types of tissues in the body. A few distinct cell types and densely packed fibers in a matrix characterize these tissues. It comprises a diverse group of cells that can be found in different parts of the body. However connective tissue differs from other types. Fill out the blanks next to your drawing. The organic matrix is similar to the matrix material found in other connective tissues, including some amount of collagen and elastic fibers. Web autoimmune connective tissue disorders comprise polymyositis, dermatomyositis, vasculitis, systemic lupus erythematosus, sjogren's syndrome, rheumatoid arthritis, and scleroderma, among others. Obtain a slide of a large artery with elastic connective. Obtain a slide of a large artery with elastic connective tissue from the slide box. Slide 36 (aorta, aldehyde fuchsin) view virtual slide. Cells, protein fibers, and an amorphous ground substance.together the fibers and ground substance make up the extracellular matrix.whereas the other tissue types. Be aware that there are many ways to categorize connective tissues, and, in some cases,. As its name implies, connective tissue is a term given to several body tissues that connect, support, and help bind other tissues. Web connective tissue is one of the basic tissue types of the body. Slide 36 (aorta, aldehyde fuchsin) view virtual slide. Connective tissues provide adhesion as well as the connection between different tissues and organs of the body.. It comprises a diverse group of cells that can be found in different parts of the body. While the various connective tissues of the body are diverse, they share numerous structural and functional features that explain why they are. • learn the diversity of this tissue group along with the common characteristics. Web elastic connective tissue 40x human aorta c.s.. A few distinct cell types and densely packed fibers in a matrix characterize these tissues. Slide 88 (aorta, h&e) view virtual slide Web obtain a slide of hyaline cartilage connective tissue from the slide box. Web sc 2115 anatomy and physiology i. The organic matrix is similar to the matrix material found in other connective tissues, including some amount of. Like all tissue types, it consists of cells surrounded by a compartment of fluid called the extracellular matrix (ecm). Web elastic connective tissue: Web of course, there are some places where there are breaks in the dense regular connective tissue of the tendon containing loose connective tissue associated with nerves and blood vessels or the occasional bit of adipose tissue.. While the various connective tissues of the body are diverse, they share numerous structural and functional features that explain why they are. Connective tissues like bones and cartilage provide structure and internal support to different parts of the body. Elastic fibers differ from collagen in the ease with which they stretch and recoil. Slide 88 (aorta, h&e) view virtual slide. Cells, protein fibers, and an amorphous ground substance.together the fibers and ground substance make up the extracellular matrix.whereas the other tissue types. Slide 88 (aorta, h&e) view virtual slide Obtain a slide of a large artery with elastic connective tissue from the slide box. Web elastic connective tissue 40x human aorta c.s. This image shows a portion of the wall. Fill out the blanks next to your drawing. Elastic fibers differ from collagen in the ease with which they stretch and recoil. Slide 36 (aorta, aldehyde fuchsin) view virtual slide. Web autoimmune connective tissue disorders comprise polymyositis, dermatomyositis, vasculitis, systemic lupus erythematosus, sjogren's syndrome, rheumatoid arthritis, and scleroderma, among others. Summary of the properties of the major types of connective. This image shows a portion of the wall of the aorta, the large vessel that carries. Web autoimmune connective tissue disorders comprise polymyositis, dermatomyositis, vasculitis, systemic lupus erythematosus, sjogren's syndrome, rheumatoid arthritis, and scleroderma, among others. Like all tissue types, it consists of cells surrounded by a compartment of fluid called the extracellular matrix (ecm). (a) dense regular connective tissue consists of collagen fibers packed into parallel bundles. A few distinct cell types and densely packed fibers in a matrix characterize these tissues. In the circle below, draw a representative sample of key features you identified, taking care to correctly and clearly draw their true shapes and directions. In bone, the matrix is rigid and described as calcified because of the deposited calcium salts. Collagenous fibersare made of collagen and consist of bundles of fibrils that are coils of collagenmolecules. Web functions of connective tissue. Web brown adipose tissue is thermogenic, meaning that as it breaks down fats, it releases metabolic heat, rather than producing adenosine triphosphate (atp), a key molecule used in metabolism. • observe under the microscope the major connective tissues found in the body. Summary of the properties of the major types of connective tissue proper. • study the characteristics of loose, dense, elastic, and. This gives strength and flexibility to the tissue. In bone, the matrix is rigid and described as calcified because of the deposited calcium salts. Fill out the blanks next to your drawing.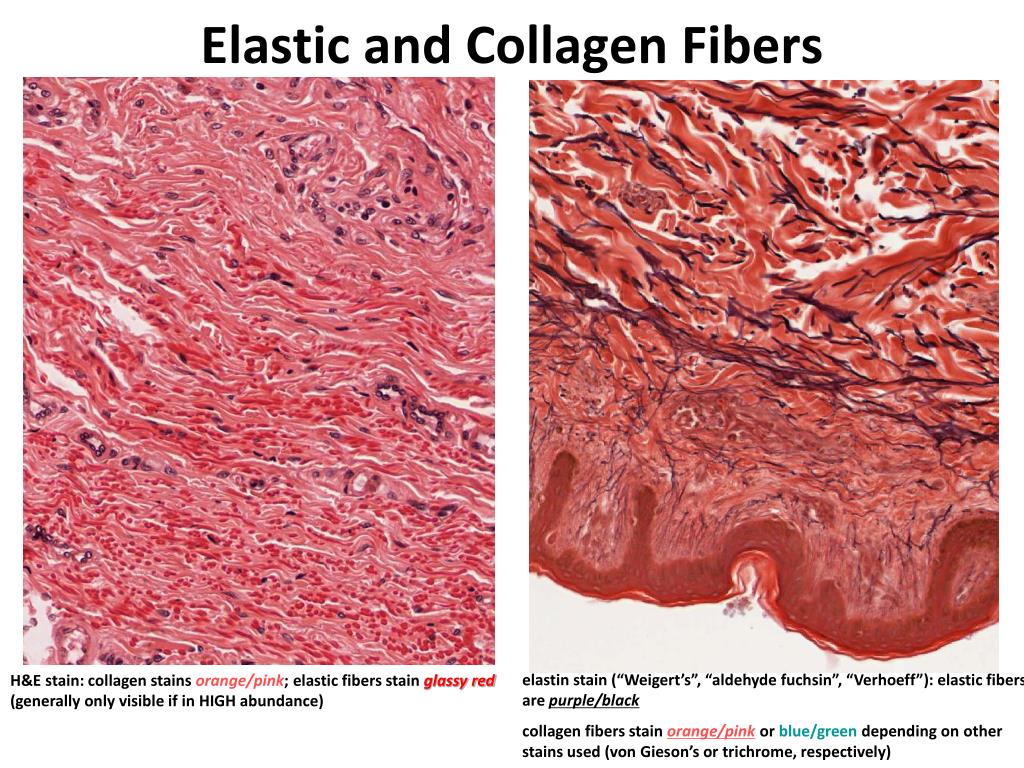
PPT Histology Connective Tissue PowerPoint Presentation, free
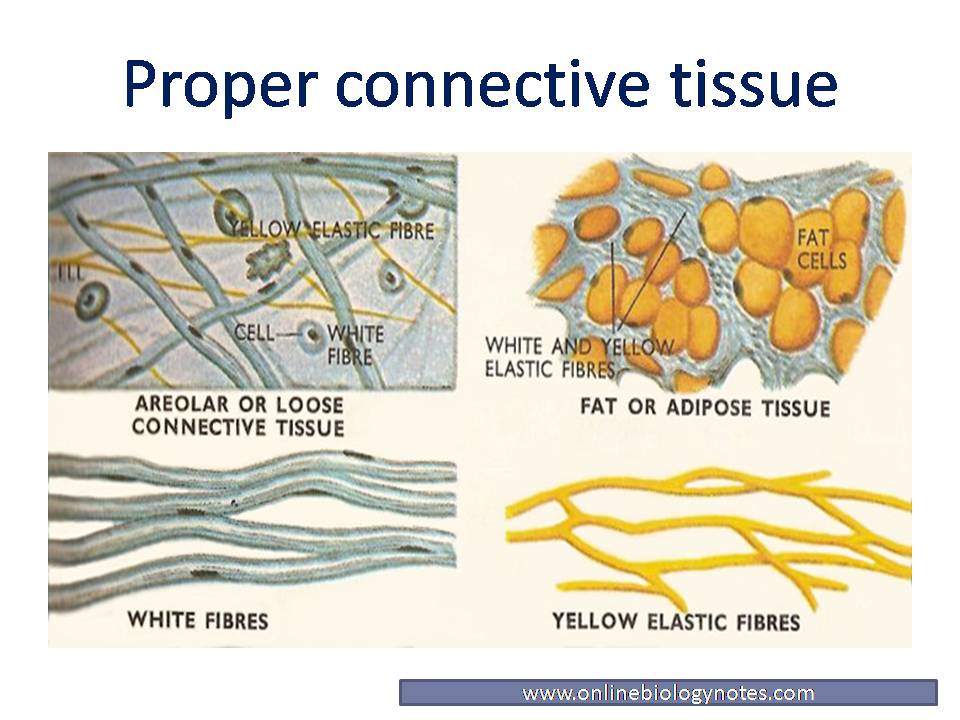
Proper connective tissue Areolar, Adipose, Reticular, white fibrous

Aorta Primate Showing Elastic Connective Tissue Stock Photo 2043968780

4.3 Connective Tissue Supports and Protects Douglas College Human
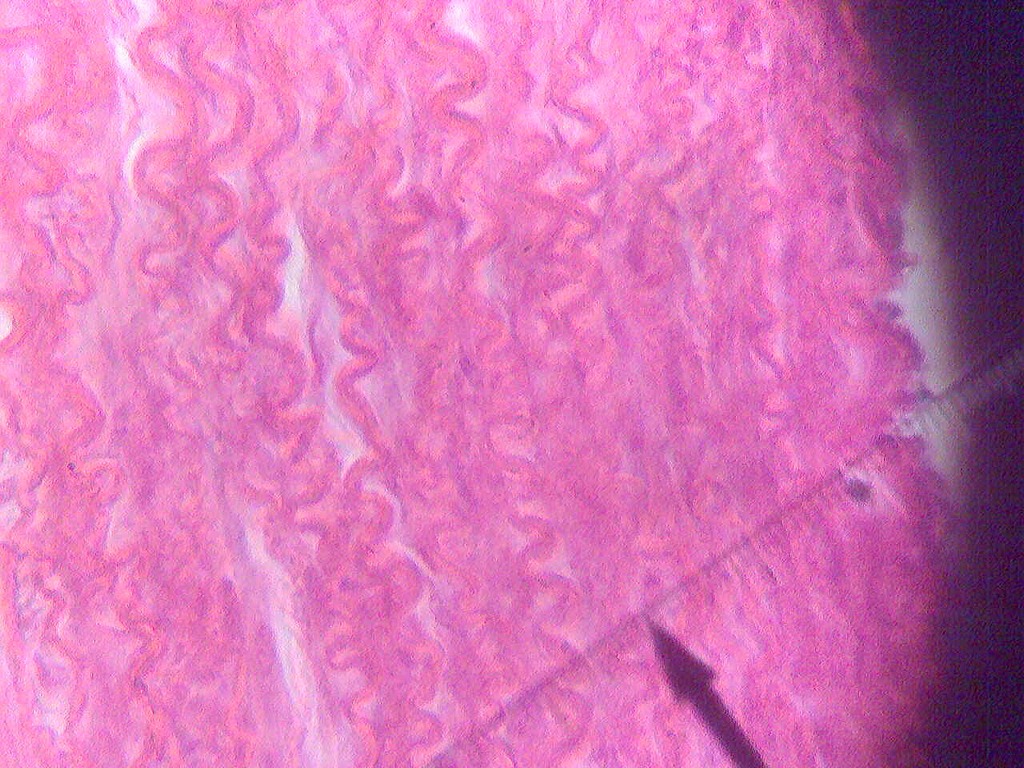
Elastic connective tissue Science, anatomy ShowMe

A&P1 Lab 3 elastic connective tissue YouTube

Connective Tissue. Structure and Anatomy Stock Vector Illustration of

Connective Tissue; Structure and Function McIsaac Health Systems Inc.
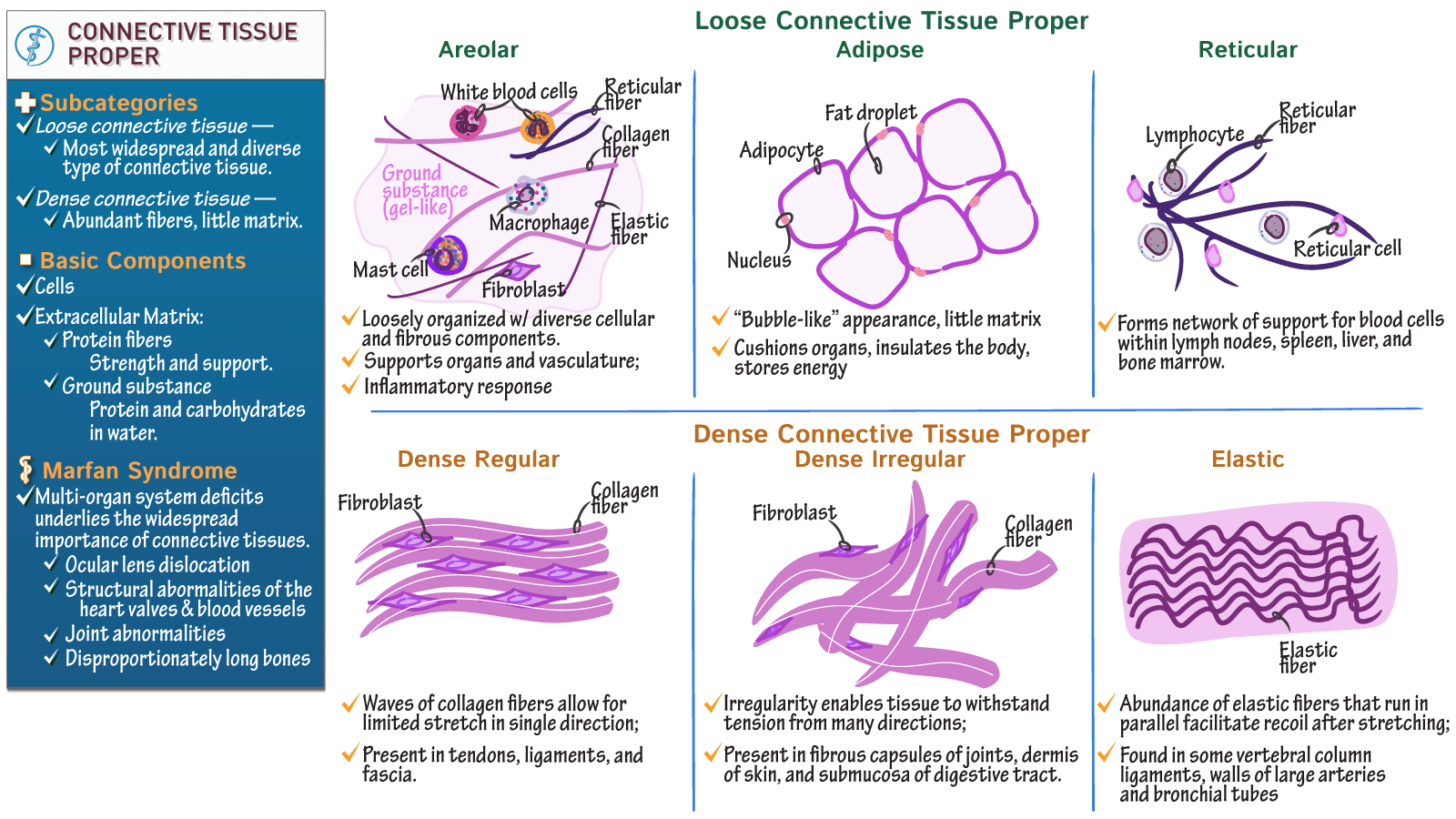
Anatomy & Physiology Connective Tissue Proper ditki medical

Connective Tissue Supports and Protects · Anatomy & Physiology
However Connective Tissue Differs From Other Types In That Its Cells Are Loosely, Rather Than Tightly, Packed.
Web Loose Connective Tissue, Also Called Areolar Connective Tissue, Has A Sampling Of All Of The Components Of A Connective Tissue.as Illustrated In Figure 1, Loose Connective Tissue Has Some Fibroblasts;
Web Connective Tissue Is The Tissue That Connects Or Separates, And Supports All The Other Types Of Tissues In The Body.
Connective Tissues Like Bones And Cartilage Provide Structure And Internal Support To Different Parts Of The Body.
Related Post: