How To Draw A Mo Diagram
How To Draw A Mo Diagram - Web how to draw molecular orbital diagrams for conjugated systems Web molecular orbital diagrams. Solution we draw a molecular orbital energy diagram similar to that shown in figure 8.37. 2h 2v d ∞h or c ∞v) (z axis is principal axis; In the third column, draw the atomic diagram for your second element. This different from nitrogen, where it's the othe. N* = # electrons in antibonding orbitals. Draw the mo diagram for `o_2^+` this is a bit of a curveball, but a perfectly valid problem. The striker was controversially sent off, following a lengthy var review, in. Web for chem videos, quizzes and more download chemistry x for free on the app store! H has a 1s orbital. Now let's put these ideas together to make an mo diagram for hf. Greater overlap = greater change in. Draw the mo for o 2: Web mo diagram for hf. N = # electrons in bonding orbitals. Molecular orbital diagrams are complex, involving two additional orbitals, electronegativity, atomic symmetries and atomic energies. Recall that a cation indicates a loss of `1` electron. Web however, recall that the more electronegative atom will be lower on the diagram. Draw two lines to create three columns. They are usually used to explore domain concepts, understand software requirements and. Web a class diagram is a uml diagram type that describes a system by visualizing the different types of objects within a system and the kinds of static relationships that exist among them. N = # electrons in bonding orbitals. Web drawing molecular orbital diagrams is one of. From this diagram, calculate the bond order for o 2. This scheme of bonding and antibonding orbitals is usually depicted by a molecular orbital diagram such as the one shown here for the dihydrogen ion h 2 +. That is, it's `o_2` with `1` missing electron. Based on the amount of orbital overlap, the relative changes in energy differ going. Bond order gives you an idea of the strength of the bond between two atoms. We need to know what orbitals we are using. Web drawing molecular orbital diagrams is one of the trickier concepts in chemistry. F has a 2s orbital and 3 2p orbitals (x,y,z). Valence bond theory and molecular. Define bond order, and state its significance.; Web below is the completed argon orbital diagram. H has a 1s orbital. Based on the amount of orbital overlap, the relative changes in energy differ going from the atomic orbital to the molecular orbital. Draw the mo diagram for `o_2^+` this is a bit of a curveball, but a perfectly valid problem. F has a 2s orbital and 3 2p orbitals (x,y,z). We are only going to consider valence orbitals. N = # electrons in bonding orbitals. We will also compare our predictions to experimental evidence. As a rule of thumb, a bond order = 1 equates to a single bond, a bond order = 2 equates to a double bond, etc. Web similar to atomic orbitals, we can write electron configuration energy diagrams for molecular orbitals (figure 9.20 “ hydrogen molecular orbital electron configuration energy diagram”).notice that the atomic orbitals of each atom are written on either side, and the newly formed molecular orbitals are written in the centre of the diagram. That is, it's `o_2` with `1` missing electron. Web. We will predict their bond order and see how the energies of the different orbitals change. In the third column, draw the atomic diagram for your second element. Web however, recall that the more electronegative atom will be lower on the diagram. Recall that a cation indicates a loss of `1` electron. Construct a qualitative molecular orbital diagram for chlorine,. This scheme of bonding and antibonding orbitals is usually depicted by a molecular orbital diagram such as the one shown here for the dihydrogen ion h 2 +. The symmetry of group orbitals is determined by reducing a reducible representation of the orbitals in question. This different from nitrogen, where it's the othe. `o_2^+` is just the ionized form of. Draw two lines to create three columns. Try the following mo's on your own, and then check with the answers provided. As a rule of thumb, a bond order = 1 equates to a single bond, a bond order = 2 equates to a double bond, etc. Make sure you thoroughly understand the following essential ideas. Web similar to atomic orbitals, we can write electron configuration energy diagrams for molecular orbitals (figure 9.20 “ hydrogen molecular orbital electron configuration energy diagram”).notice that the atomic orbitals of each atom are written on either side, and the newly formed molecular orbitals are written in the centre of the diagram. Draw the mo diagram for `o_2^+` this is a bit of a curveball, but a perfectly valid problem. Describe the essential difference between a sigma and a pi molecular orbital.; Draw the mo for o 2: For this example, we will be using chlorine. That is, it's `o_2` with `1` missing electron. Web when two oxygen atoms overlap, the sigma(2p) molecular orbital is lower in energy than the pi(2p) orbitals. The mo diagram will be the same as the mo diagram of `o_2`, except with `1` less electron. The first major step is understanding the difference between two major theories: `o_2^+` is just the ionized form of `o_2`; Assign x, y, z coordinates and c instead of. The striker was controversially sent off, following a lengthy var review, in.
How to Draw Molecular Orbital Diagrams (MO DIAGRAMS) Explanation YouTube
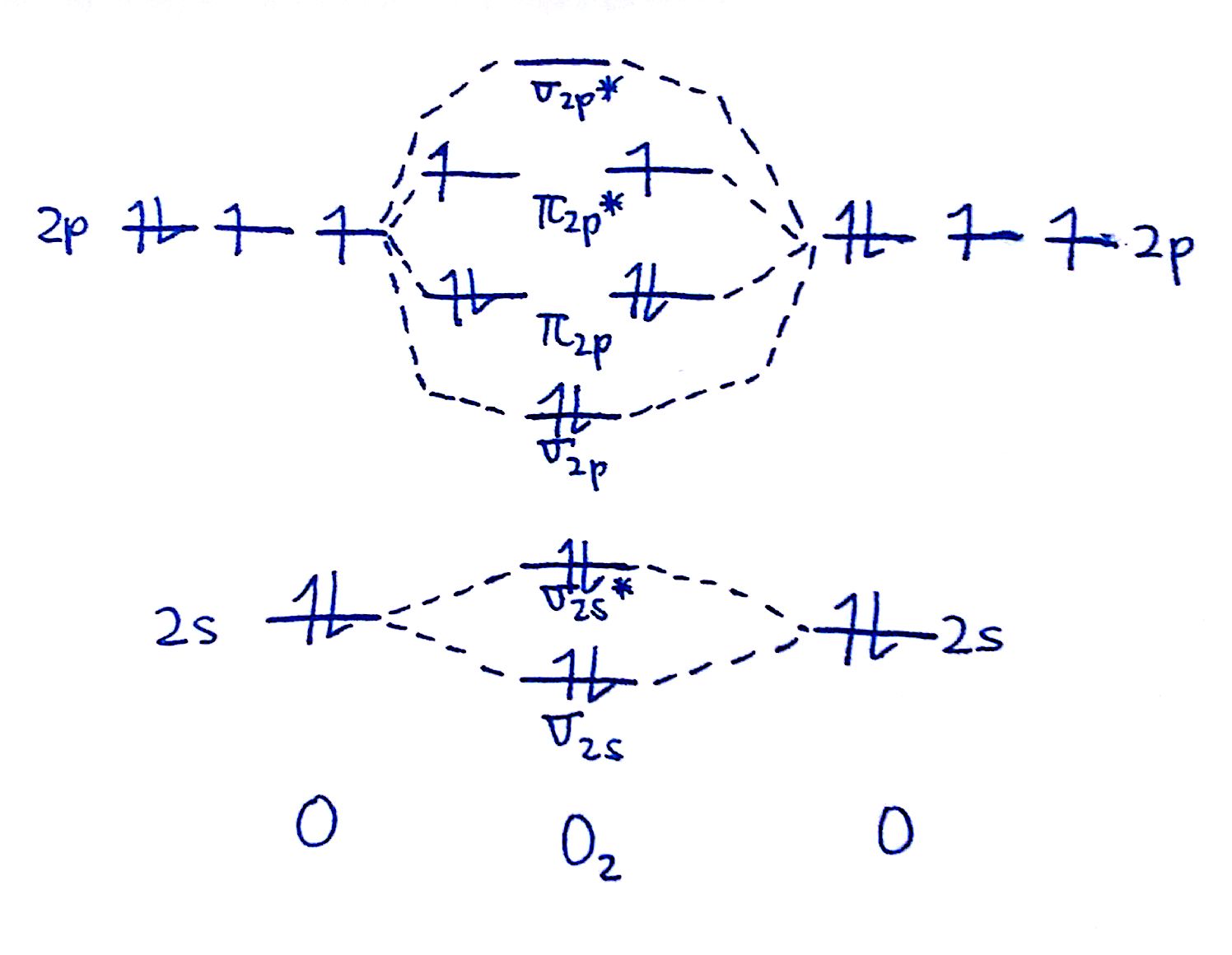
MO Diagrams

SF6 Lewis Structure, Molecular Geometry, Hybridization, and MO Diagram

9.8 Molecular Orbital Theory Chemistry Libretexts 22B
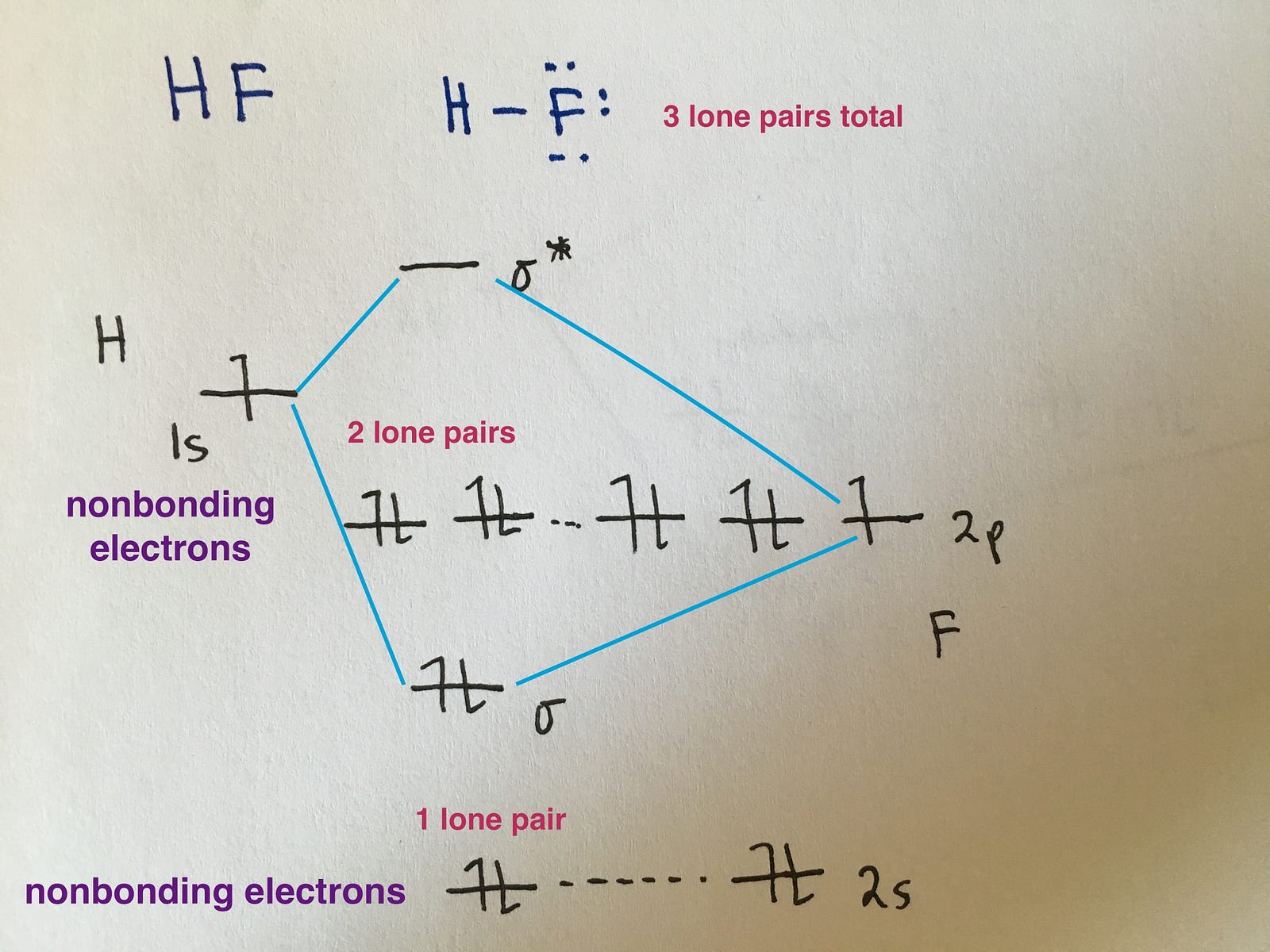
How To Draw Mo Diagram Wiring Site Resource
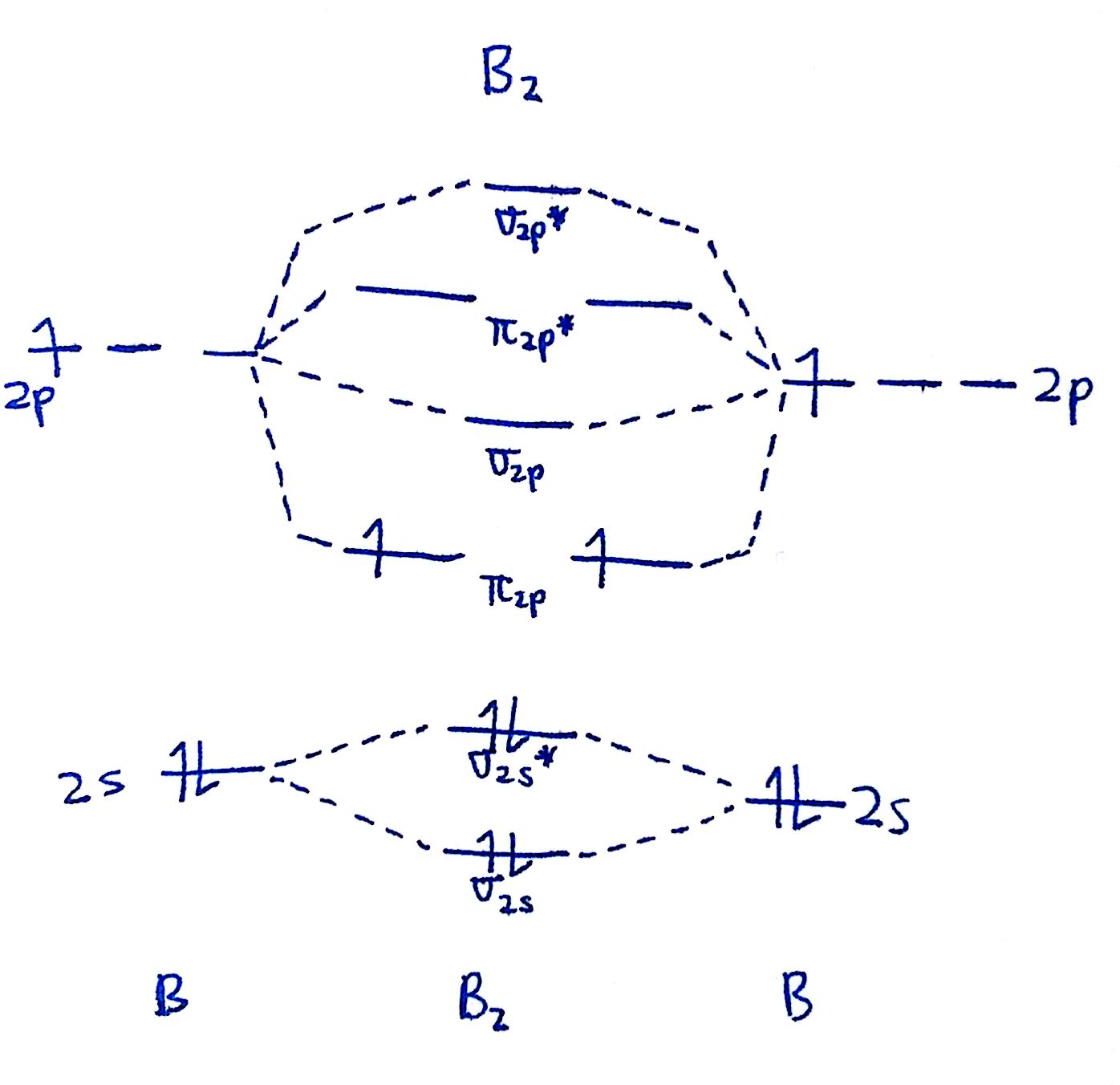
MO Diagrams

MO Diagram Overview, How to draw MO Diagram and Solved example along
MO Diagrams for First Row Diatomic Molecules Chemistry LibreTexts

how to draw molecular orbital diagrams for polyatomic molecules

MO Diagram Overview, How to draw MO Diagram and Solved example along
We Are Only Going To Consider Valence Orbitals.
This Approach Is Used Only When The Group Orbitals Are Not Obvious By Inspection.
We Need To Know What Orbitals We Are Using.
This Different From Nitrogen, Where It's The Othe.
Related Post: