Muscle Contraction Drawing
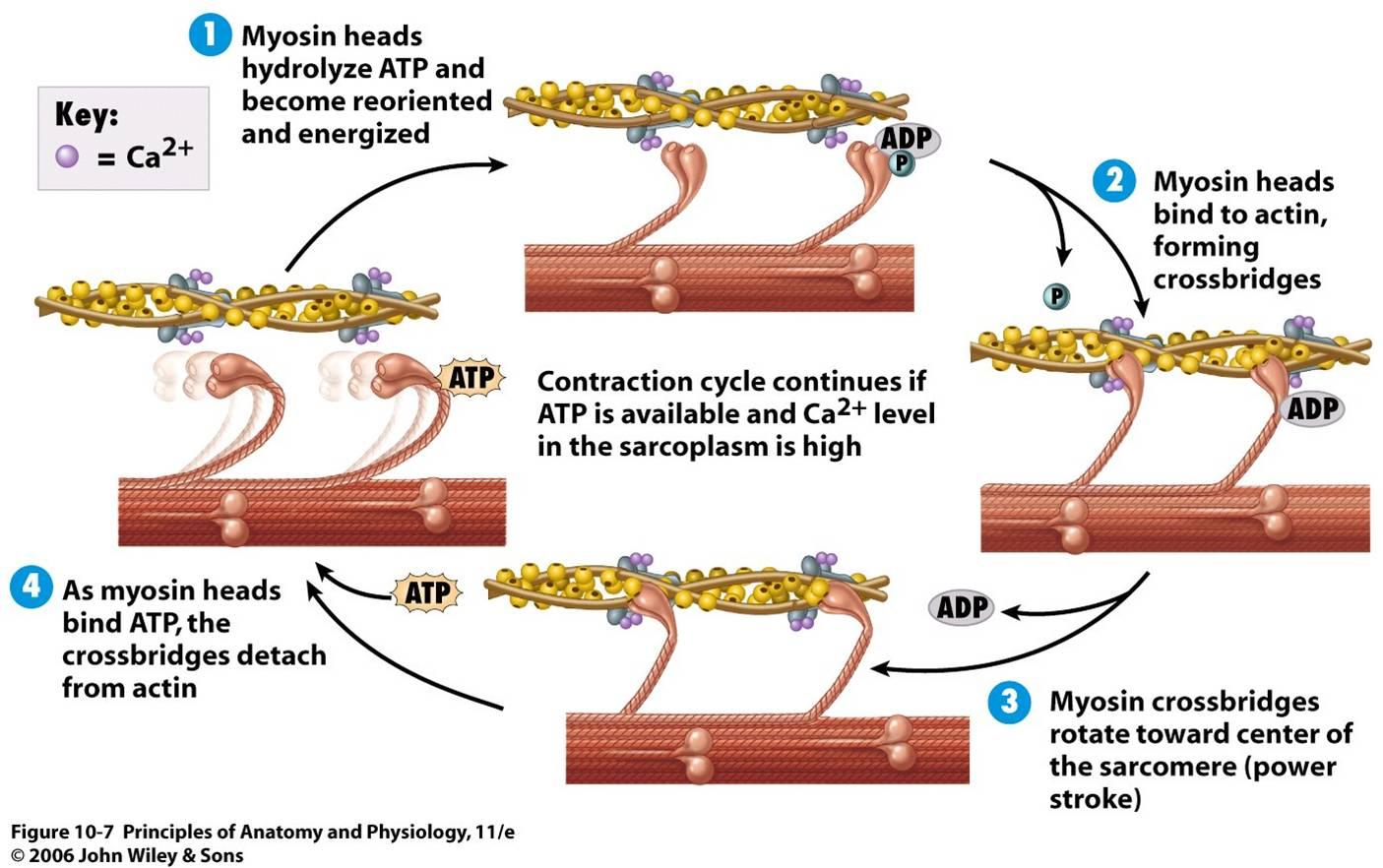
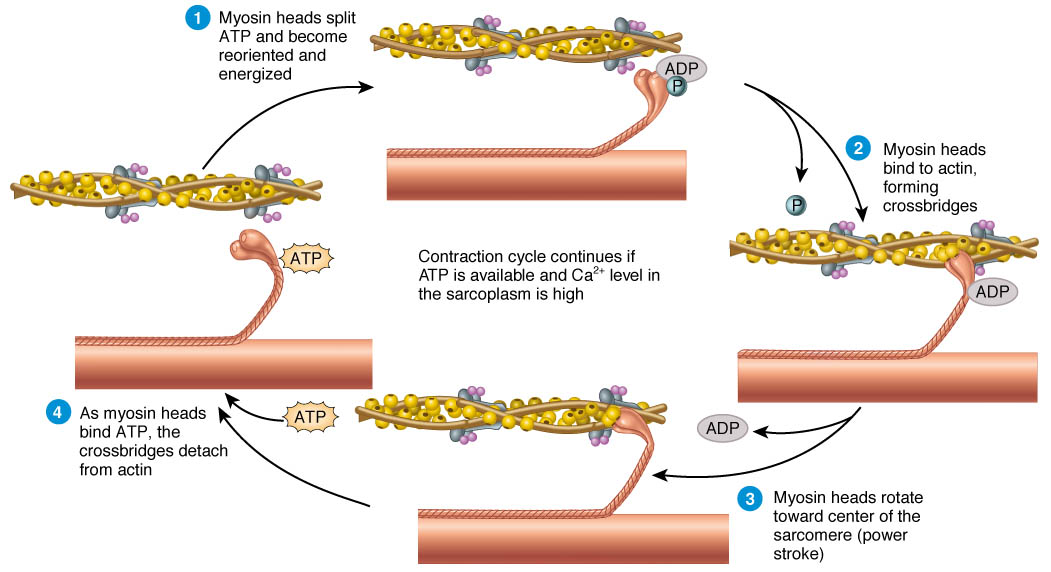
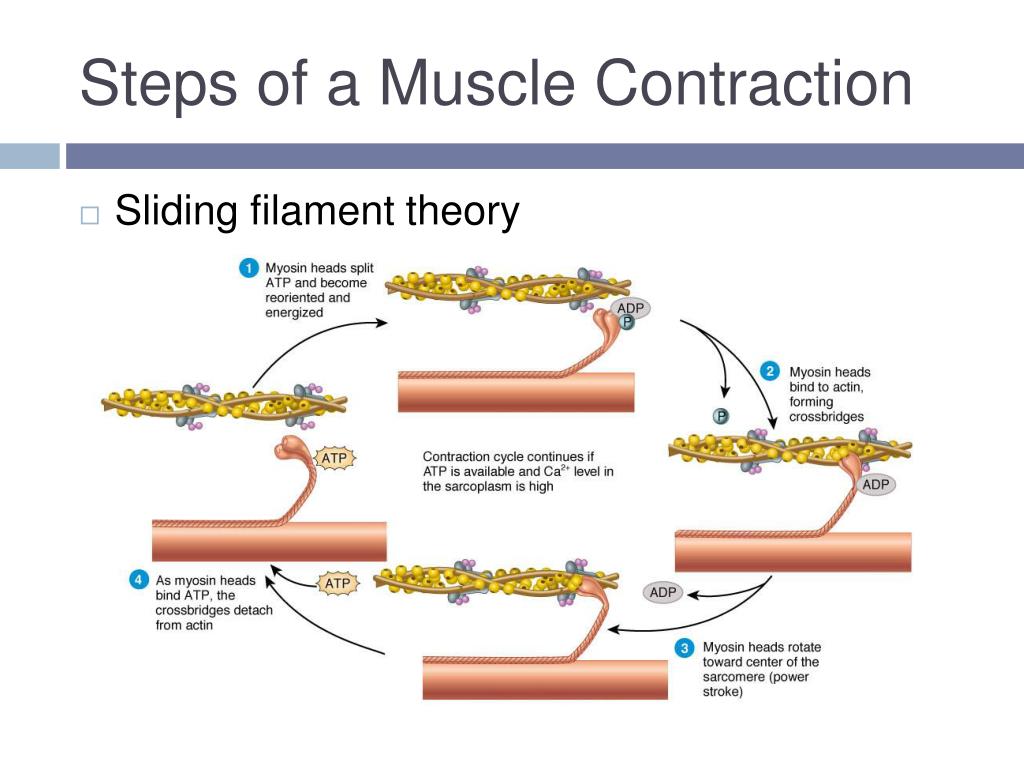
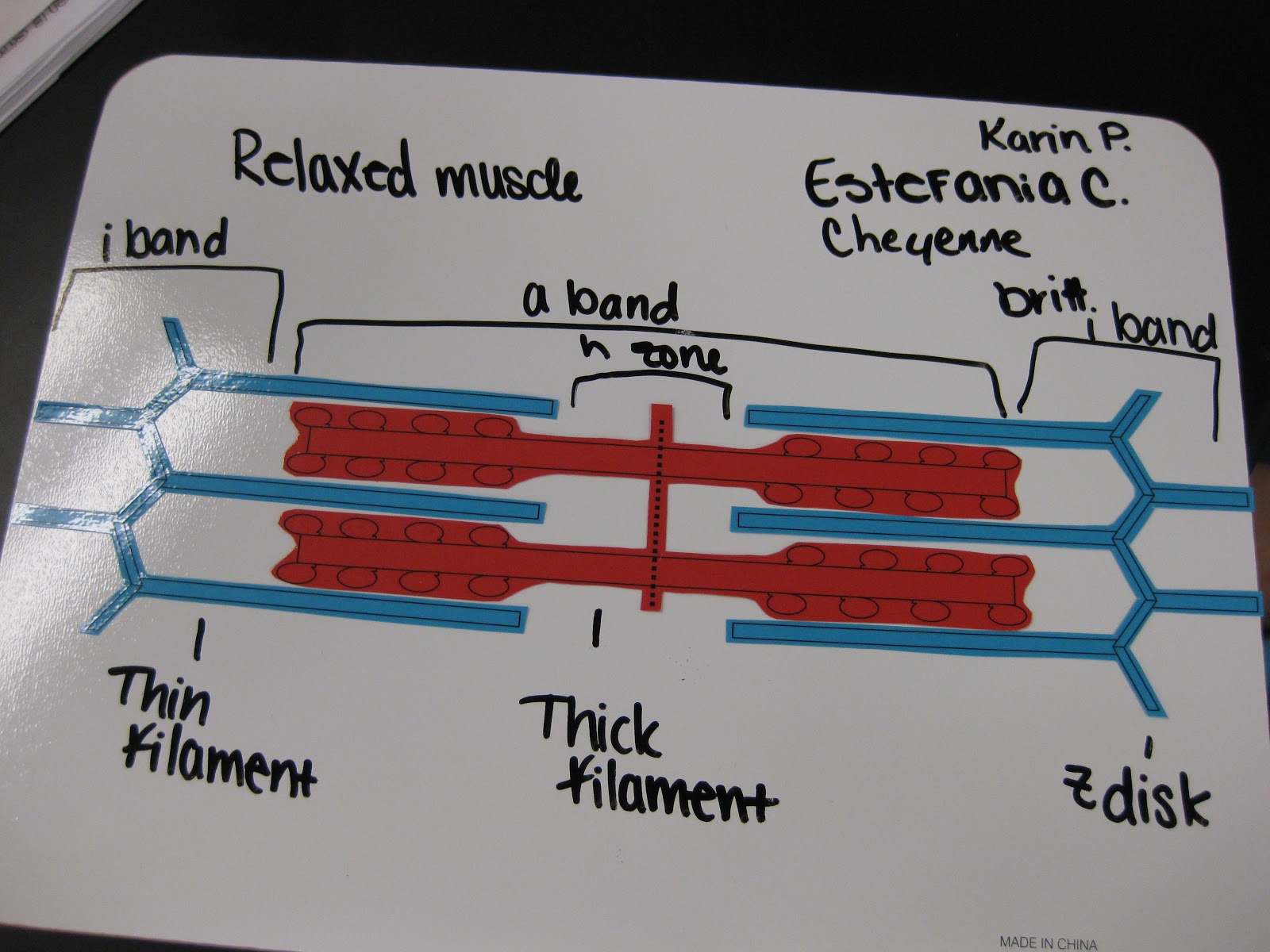
Muscle Contraction Drawing - This process either shortens the muscle or increases its tension, generating a force that either facilitates or slows down a movement. The physiological concept of muscle contraction is based on two variables: This is a key part of how muscles function, converting chemical energy into mechanical energy. Web describe the components involved in a muscle contraction; Join the amoeba sisters a they explore different muscle tissues and then focus on the sliding filament theory in skeletal muscle! Web how do the bones of the human skeleton move? Web describe the sliding filament model of muscle contraction. During contraction, myosin myofilaments ratchet over actin myofilaments contracting the sarcomere. Learn how proteins, specifically myosin and actin, use atp to produce movement in muscles. Web muscle contraction is initiated with the depolarization of the sarcolemma caused by the sodium ions' entrance through the sodium channels associated with the ach receptors. Web it is classified as a striated muscle tissue, which functions to contract and permit movements under voluntary control. The sarcomere is the region in which sliding filament contraction occurs. Describe the sliding filament model of muscle contraction. Web choose from muscle contraction drawing stock illustrations from istock. The physiological concept of muscle contraction is based on two variables: Web muscle contraction occurs as a result of the interaction of myofibrils inside the muscle cells. The number of motor units involved in contraction and the amount of stimulus from the nervous system. Explain how smooth muscle differs from skeletal muscle. Describe the components involved in a muscle contraction. Web choose from muscle contraction drawing stock illustrations from istock. Describe the components involved in a muscle contraction. Explain how smooth muscle differs from skeletal muscle. Web it is classified as a striated muscle tissue, which functions to contract and permit movements under voluntary control. This diagram represents the sequence of events that occurs when a motor neuron stimulates a muscle fiber to contract. You can take the amount of. This process either shortens the muscle or increases its tension, generating a force that either facilitates or slows down a movement. Web figure drawing essentials: Skeletal muscles contract and relax to mechanically move the body. As long as ca ++ ions remain in the sarcoplasm to bind to troponin, and as long as atp is available, the muscle fiber will. Web it is classified as a striated muscle tissue, which functions to contract and permit movements under voluntary control. Messages from the nervous system cause these muscle contractions. Web muscle contraction is initiated with the depolarization of the sarcolemma caused by the sodium ions' entrance through the sodium channels associated with the ach receptors. This video also briefly tal. By. Web explain the process of smooth muscle contraction. During contraction, myosin myofilaments ratchet over actin myofilaments contracting the sarcomere. This process either shortens the muscle or increases its tension, generating a force that either facilitates or slows down a movement. The a band stays the same width. At full contraction, the thin and thick filaments have the most amount of. It’s a complex puzzle of bones and muscles that gives life and energy to every pose we draw. Web choose from muscle contraction drawing stock illustrations from istock. The a band stays the same width. Explain how muscles contract and relax; 23 september 2023 by proactive creative. The whole process is called the mechanism of muscle contraction and it can be summarized in three steps: You can take the amount of force of each actin myosin pair (from wikipedia) and multiply it to check the actual forces produced. A single nerve impulse of a motor neuron will cause a motor unit to contract briefly before relaxing. Web. The sarcomere is the region in which sliding filament contraction occurs. Join the amoeba sisters a they explore different muscle tissues and then focus on the sliding filament theory in skeletal muscle! In physiology, muscle shortening and muscle contraction are not synonymous. Web muscle contraction occurs as a result of the interaction of myofibrils inside the muscle cells. The sarcomere. Web muscle contraction requires energy, and when atp is broken down, heat is produced. Describe the sliding filament model of muscle contraction. Understand the role of atp hydrolysis in this process. Web figure drawing essentials: Learn how proteins, specifically myosin and actin, use atp to produce movement in muscles. Web by studying sarcomeres, the basic unit controlling changes in muscle length, scientists proposed the sliding filament theory to explain the molecular mechanisms behind muscle contraction. Web this is known as the sliding filament model of muscle contraction and occurs via the following process: Web explain the process of smooth muscle contraction. You can take the amount of force of each actin myosin pair (from wikipedia) and multiply it to check the actual forces produced. The sarcomere is the region in which sliding filament contraction occurs. During contraction, myosin myofilaments ratchet over actin myofilaments contracting the sarcomere. Describe the sliding filament model of muscle contraction. This article will discuss the structure of skeletal muscle tissue, it’s mode of contraction and relevant clinical conditions. A single nerve impulse of a motor neuron will cause a motor unit to contract briefly before relaxing. Explain how muscles contract and relax. Web muscle contraction is initiated with the depolarization of the sarcolemma caused by the sodium ions' entrance through the sodium channels associated with the ach receptors. This is a key part of how muscles function, converting chemical energy into mechanical energy. In physiology, muscle shortening and muscle contraction are not synonymous. Describe the sliding filament model of muscle contraction Messages from the nervous system cause these muscle contractions. Understand the role of atp hydrolysis in this process.
Muscle Contraction Cycle Muscular system anatomy, Basic anatomy and

Muscle Contraction Vector & Photo (Free Trial) Bigstock
My Awe of the Human Body Muscle Movement My Kind of Science
Sliding Filament Theory of Muscle Contraction Online Biology Notes
steps of muscle contraction anatomy
What Did You Do Today at School? Muscle Contraction Modeling

Muscle contraction Higher Level Biology IB

6.4 Muscle Contraction Medicine LibreTexts

Muscle Contraction Diagram (labelled) Stock Image C043/4842

Anatomy Muscle Contraction Anatomical Charts & Posters
Web Describe The Sliding Filament Model Of Muscle Contraction.
An Action Potential Arrives At The Neuromuscular Junction.
The Sarcomere Is The Region In Which Sliding Filament Contraction Occurs.
This Heat Is Very Noticeable During Exercise, When Sustained Muscle Movement Causes Body Temperature To Rise, And In Cases Of Extreme Cold, When Shivering Produces Random Skeletal Muscle Contractions To Generate Heat.
Related Post: