Pharynx Drawing
Pharynx Drawing - It also forms part of the upper respiratory tract. Web the pharynx (plural: This article explains the structure and function of the pharynx. Web the pharynx is a hollow, muscular tube inside the neck that starts behind the nose and opens into the larynx and esophagus. Your pharynx (throat) is in the middle of your neck. Essentially, it forms a continuous muscular passage for air, food, and liquids to travel down from your nose and mouth to your lungs and stomach. Web in this section, you will examine the anatomy and functions of the three main organs of the upper alimentary canal—the mouth, pharynx, and esophagus—as well as three associated accessory organs—the tongue, salivary glands, and teeth. Web the pharynx is a muscular tube that starts at the base of the skull behind the nasal cavity and extends down to the larynx (voice box) and esophagus (the tube that leads to the stomach). Web the pharynx is a conductive structure located in the midline of the neck. Web this model is used as a teaching aid to help identify the anatomical structures of the pharynx and the floor of the mouth. It is found in vertebrates and invertebrates, though. Web the pharynx is a conductive structure located in the midline of the neck. Where is the pharynx located. Web the pharynx is a hollow, muscular tube inside the neck that starts behind the nose and opens into the larynx and esophagus. This article explains the structure and function of the pharynx. Web the pharynx is a hollow, muscular tube inside the neck that starts behind the nose and opens into the larynx and esophagus. The uvula controls the passage of oxygen at the entrance of the pharynx, towards the larynx, enabling the emission of sounds. Pharynges or pharynxes) is the superior dilated part of the alimentary tract that connects the nasal. Web the pharynx (plural: The uvula controls the passage of oxygen at the entrance of the pharynx, towards the larynx, enabling the emission of sounds. The pharynx chamber serves both respiratory and digestive functions. The three parts of the pharynx are the nasopharynx, oropharynx, and hypopharynx. Essentially, it forms a continuous muscular passage for air, food, and liquids to travel. Web in this section, you will examine the anatomy and functions of the three main organs of the upper alimentary canal—the mouth, pharynx, and esophagus—as well as three associated accessory organs—the tongue, salivary glands, and teeth. It includes (inset) your nasopharynx, oropharynx and laryngopharynx. Pharynges) is the part of the throat behind the mouth and nasal cavity, and above the. The pharynx is comprised of three parts (superior to inferior): The pharynx consists of the nasopharynx, oropharynx and laryngopharynx. Where is the pharynx located. The three parts of the pharynx are the nasopharynx, oropharynx, and hypopharynx. Web the pharynx (plural: Web the pharynx is a muscular column that runs between the oral cavity and the esophagus. Web the pharynx (plural: It is the main structure, in addition to the oral cavity, shared by two organ systems, i.e., the gastrointestinal tract (git) and the respiratory system. Essentially, it forms a continuous muscular passage for air, food, and liquids to travel down. It includes (inset) your nasopharynx, oropharynx and laryngopharynx. It’s located posterior to the nasal and oral cavities and it extends inferiorly past the larynx, where it. Where is the pharynx located. It also forms part of the upper respiratory tract. It begins at the base of the skull and ends at the inferior border of the cricoid cartilage (c6). Web the pharynx is a muscular tube that connects the oral and nasal cavity to the larynx and oesophagus. All three of these cavities open posteriorly into the pharyngeal tube. Web this model is used as a teaching aid to help identify the anatomical structures of the pharynx and the floor of the mouth. The uvula controls the passage of. These fully annotated anatomical illustrations are presented as a comprehensive atlas of the oral cavity, specially designed for medical students, medicine residents and healthcare professionals. It is the main structure, in addition to the oral cavity, shared by two organ systems, i.e., the gastrointestinal tract (git) and the respiratory system. The pharynx is comprised of three parts (superior to inferior):. Web the pharynx is a hollow, muscular tube inside the neck that starts behind the nose and opens into the larynx and esophagus. Web the pharynx is a muscular tube that connects the oral and nasal cavity to the larynx and oesophagus. It begins at the base of the skull and ends at the inferior border of the cricoid cartilage. It is a musculomembranous tube, somewhat conical in form, with the base upward, and the apex downward, extending from the under surface of the skull to the level of the cricoid cartilage in front, and that of the sixth. Pharynges) is the part of the throat behind the mouth and nasal cavity, and above the esophagus and trachea (the tubes going down to the stomach and the lungs respectively). Web the pharynx is a muscular tube that starts at the base of the skull behind the nasal cavity and extends down to the larynx (voice box) and esophagus (the tube that leads to the stomach). Web the pharynx is a muscular column that runs between the oral cavity and the esophagus. The pharynx is that part of the digestive tube which is placed behind the nasal cavities, mouth, and larynx. Web @easyanatomy4ug902 pharynx and larynxpharynx anatomypharynx diagrampharynx pronunciationpharynx functionlarynx and pharynx functionwhat is the pharynx anat. The three parts of the pharynx are the nasopharynx, oropharynx, and hypopharynx. It’s located posterior to the nasal and oral cavities and it extends inferiorly past the larynx, where it. It is found in vertebrates and invertebrates, though. Web in this section, you will examine the anatomy and functions of the three main organs of the upper alimentary canal—the mouth, pharynx, and esophagus—as well as three associated accessory organs—the tongue, salivary glands, and teeth. Side view of head showing location of swollen and enlarged tonsils. The pharynx chamber serves both respiratory and digestive functions. It includes (inset) your nasopharynx, oropharynx and laryngopharynx. Web the pharynx extends from the cranial base to the inferior border of the cricoid cartilage anteriorly and the inferior border of the c6 vertebra posteriorly. The uvula controls the passage of oxygen at the entrance of the pharynx, towards the larynx, enabling the emission of sounds. Web the pharynx is a hollow, muscular tube inside the neck that starts behind the nose and opens into the larynx and esophagus.
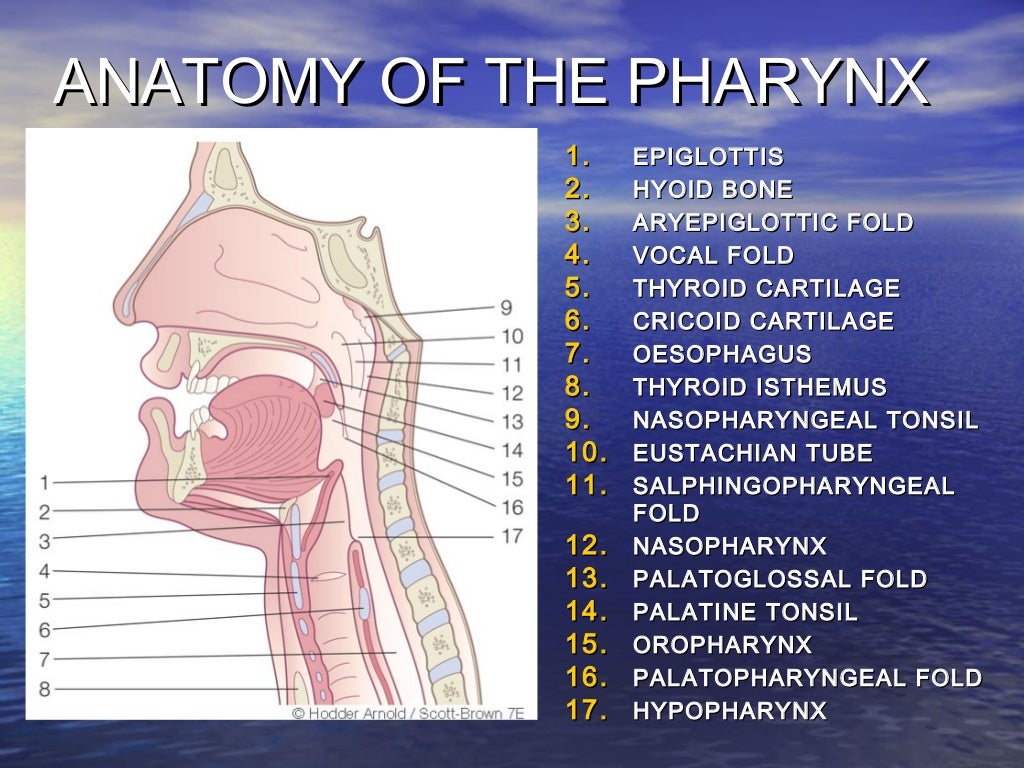
Anatomy of the Pharynx TrialExhibits Inc.
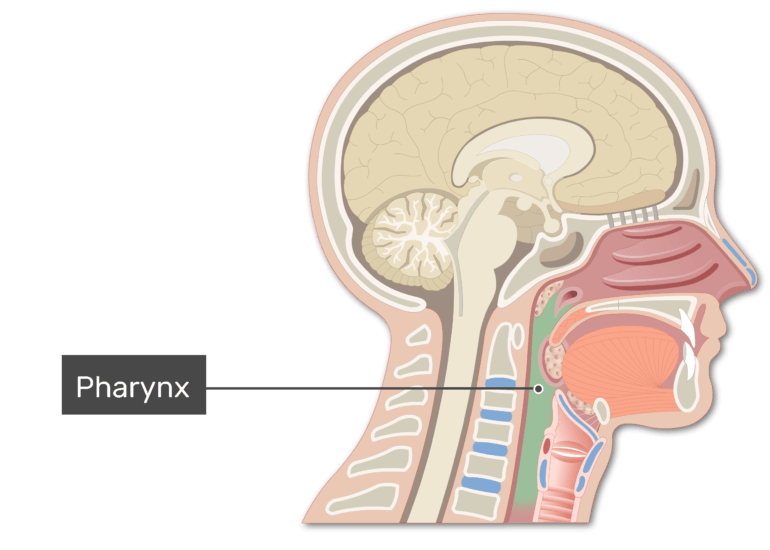
Anatomy and regions of the pharynx GetBodySmart
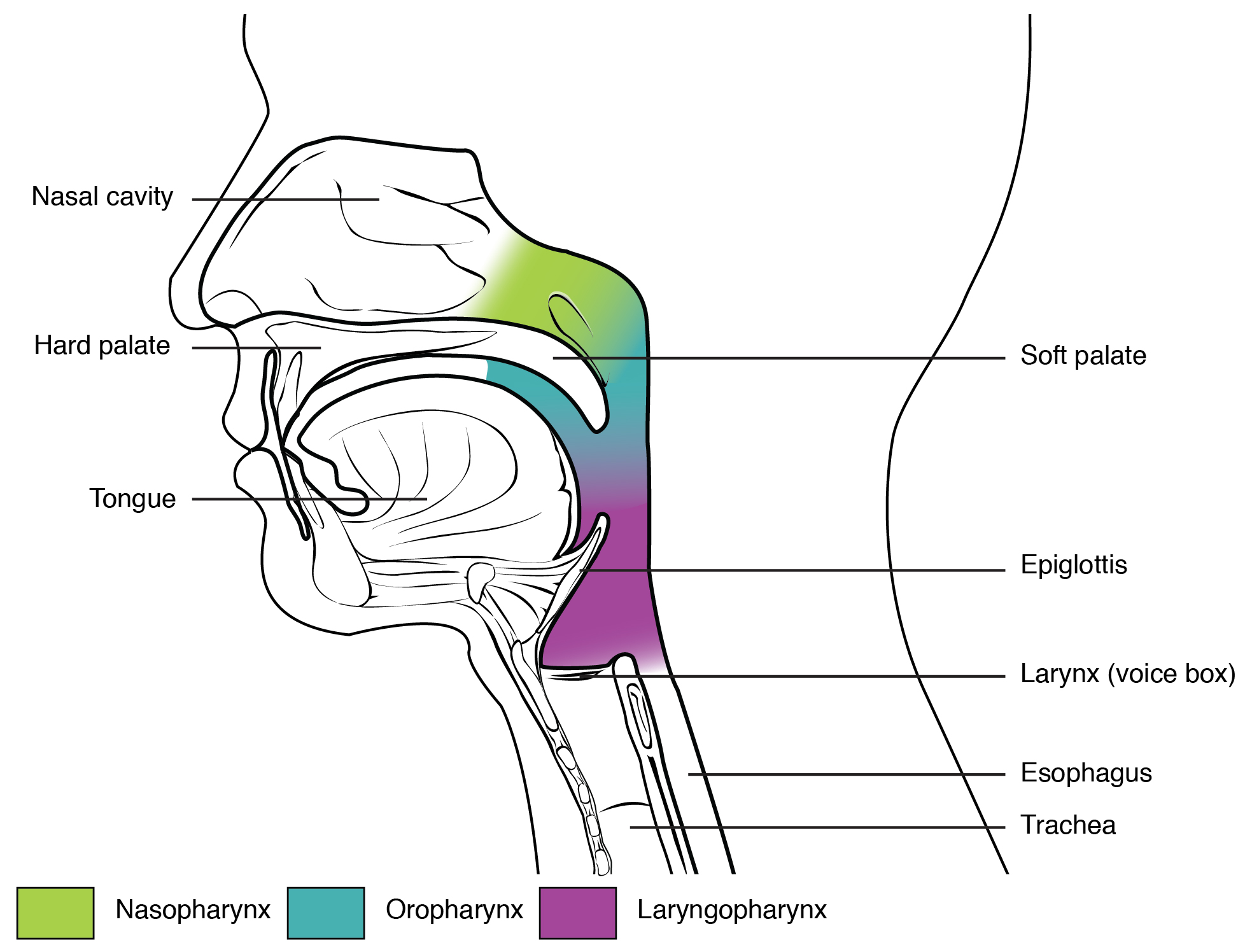
Module 26 Pharynx and Larynx Nasal Cavity and Smell Anatomy 337
/human-larynx--illustration-1190674300-4ce616b410ea488ab61b6fca58fc992b.jpg)
Larynx Anatomy, Function, and Treatment
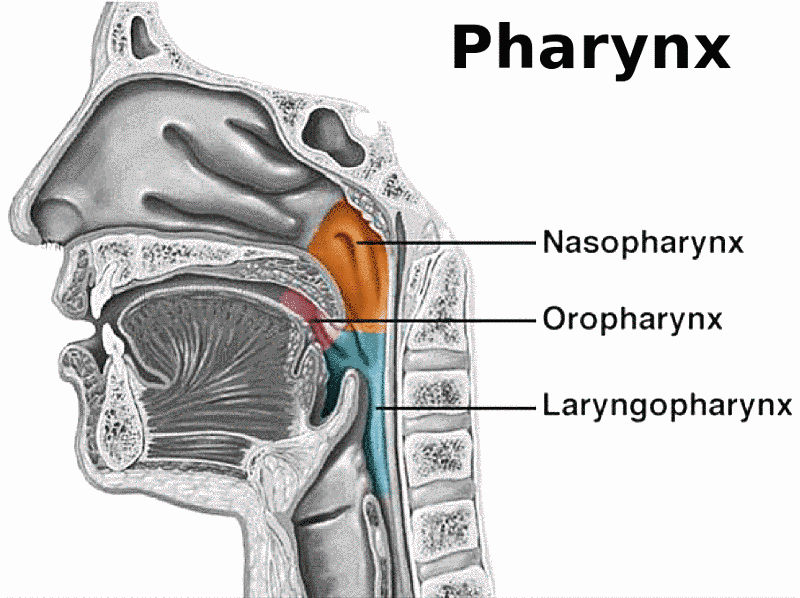
Anatomy of pharynx
Pharynx Function, Location, Anatomy, Muscles and FAQs

Regions Pharynx Throat Parts Division Cavity Stock Vector (Royalty Free

Normal anatomy of the pharynx Download Scientific Diagram
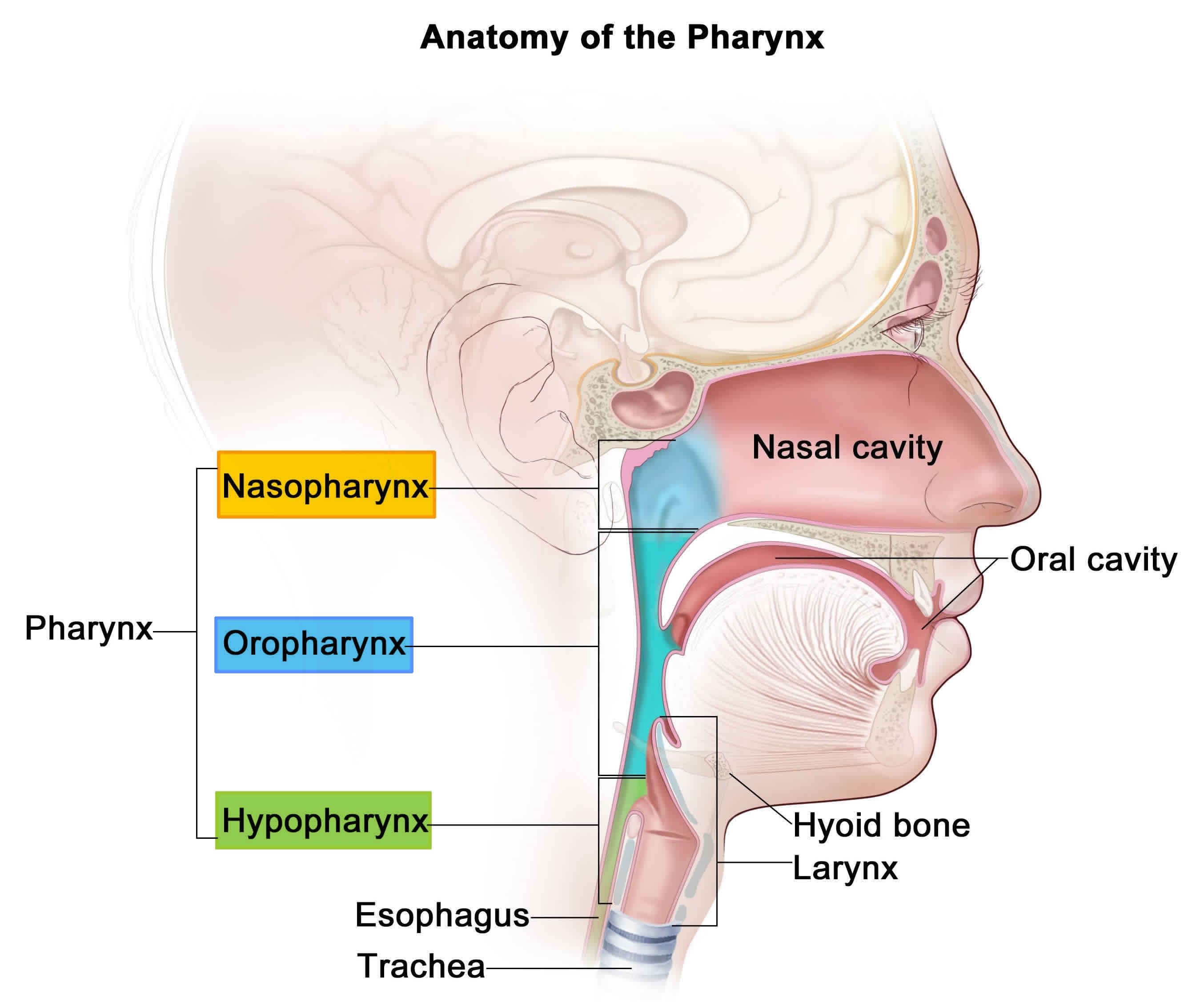
Pharynx Anatomy & Function in Respiratory System
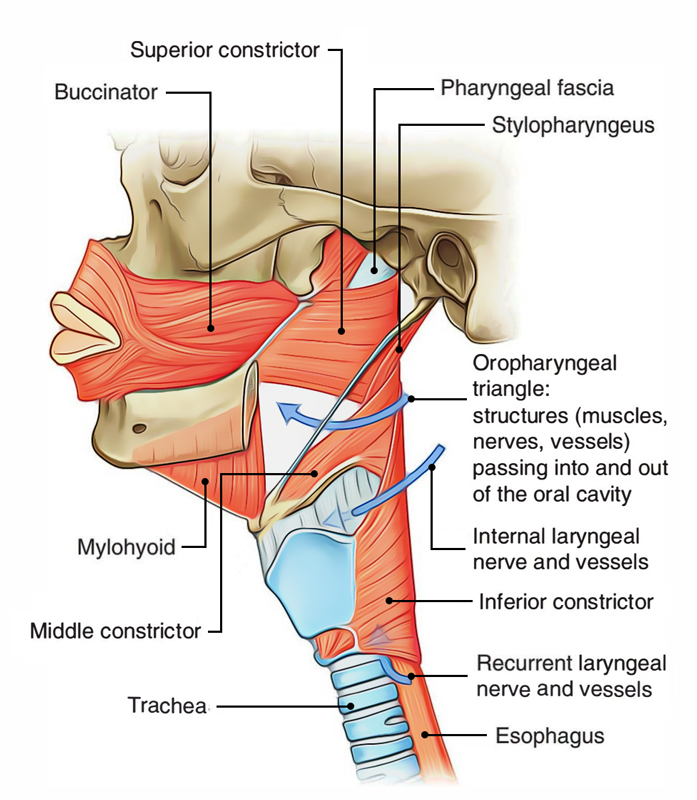
Pharynx Earth's Lab
Essentially, It Forms A Continuous Muscular Passage For Air, Food, And Liquids To Travel Down From Your Nose And Mouth To Your Lungs And Stomach.
Web This Model Is Used As A Teaching Aid To Help Identify The Anatomical Structures Of The Pharynx And The Floor Of The Mouth.
It Is The Main Structure, In Addition To The Oral Cavity, Shared By Two Organ Systems, I.e., The Gastrointestinal Tract (Git) And The Respiratory System.
Your Pharynx (Throat) Is A Multitasking Muscular Funnel That Helps You Breathe And Directs Food And Liquid To Your Digestive System.
Related Post: